Cloud Based Patch Management
Cloud Based Patch Management
With remote and hybrid work environments gaining prominence in recent times, apps, software, and businesses had to adapt. Cloud-based patch management tools are the ‘solution’ to this problem, and sure enough, organizations have started to incorporate and adopt cloud based solutions in the work environment.
Patch management is the process of managing a network by scanning, testing, and deploying missing patches. This is usually performed by using a patch management tool that simplifies most of the work.
What is Cloud-Based Patch Management?
Patch management software usually consist of a server that processes information and a database in which patches are stored. The location of storage of the server and database is what determines whether a solution is cloud based or on-premise. When the entire system/architecture of the patching software is on the cloud, the solution is called cloud-based patch management.
Cloud Based Patch Management Architecture
Cloud-based Server:
The central brain/processor of the architecture. This server receives info from the agents in the endpoints, syncs with the latest patches, and also provides a graphical interface for admins to work with. It also provides a centralized view of the network, and any operations performed by the admins are communicated to the agents.
Patch Repository:
An exhaustive repository that stores and continuously downloads the latest patches from vendor websites. It is connected to the agent and the server and sends the non-security and security patches to the endpoints when needed.
Agent:
A multi-functional agent that receives and sends instructions to the server and also performs them in the endpoint. It executes the necessary tasks like scanning for missing patches etc., and helps facilitate the easy functioning of the patch management solution.
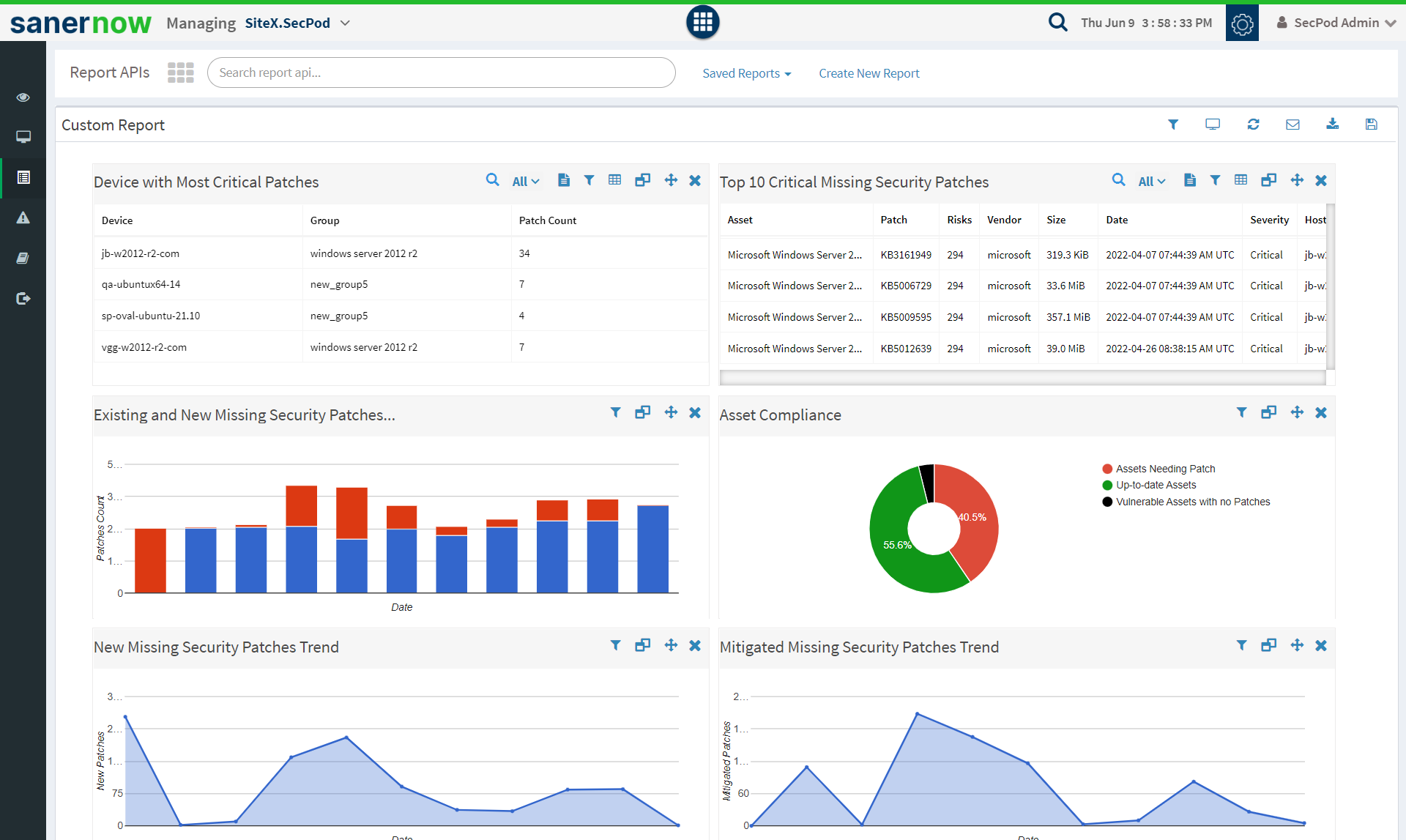
Features of Cloud based Patching Tool:
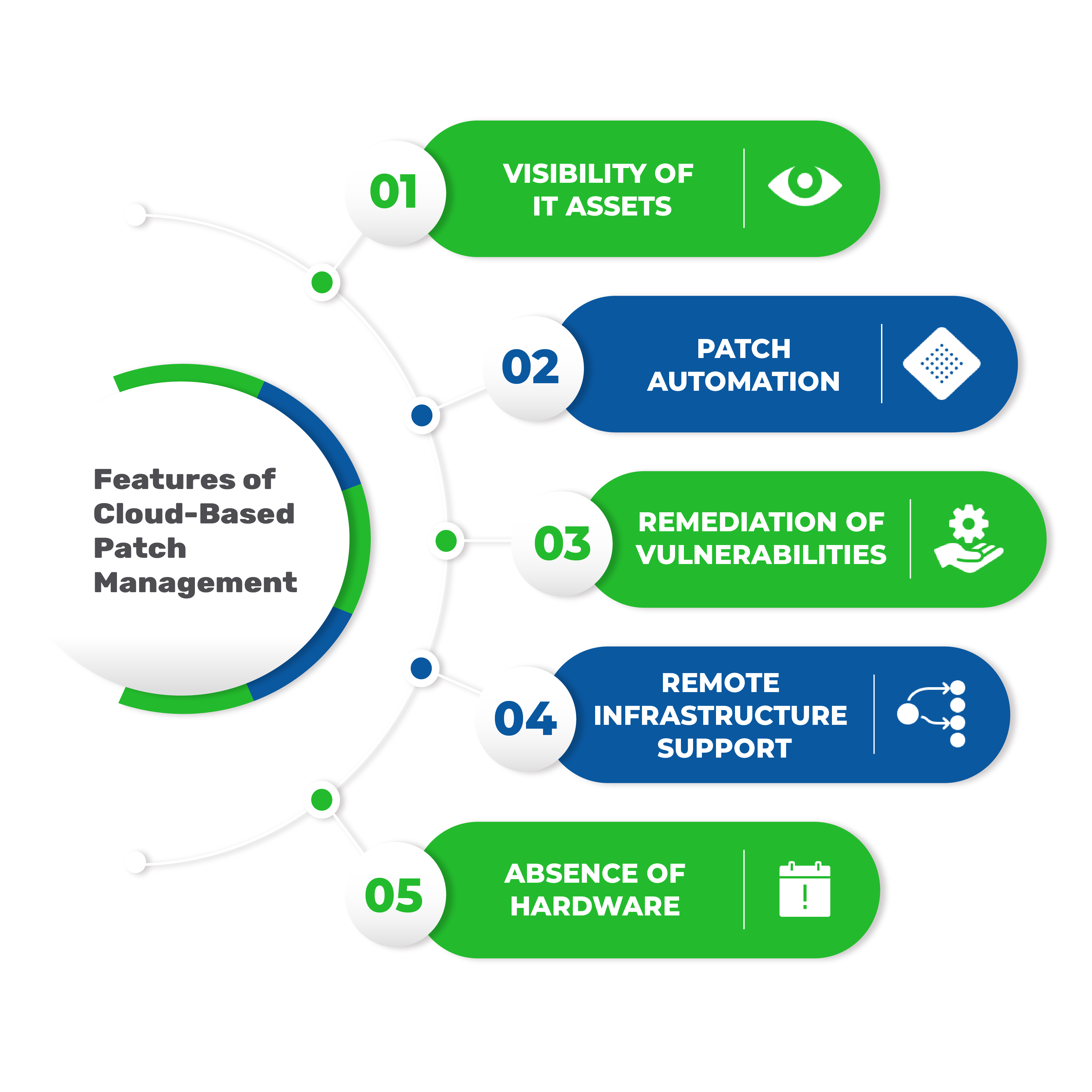
Visibility of IT assets:
Patching tools scan throughout the network, so along with the info about patches, it also provides an overview of the entire network as well. This visibility is essential in getting an insight into what’s happening in the network as well. It helps in accurately tracking assets, licenses, and more.
Patch Automation:
Automation is an essential key feature in any patch management tool. Clicking ‘apply patch’ on too many apps and too many patches can become difficult in the long run. But with auto patching, most of the difficult and bothering steps become simpler and a one-time effort.
Remediation of Vulnerabilities:
Patches fix vulnerabilities alongside many other things like new features and more. Just like an on-premise patching solution, cloud based patching also performs patching, which fixes bugs and vulnerabilities. So, proper application of patches leads to reduced attack surface by remediating critical vulnerabilities.
Remote Infrastructure support:
The key difference and one of the main reasons for the large-scale adoption of cloud-based patching is the support for remote workstations scattered throughout the world. On-premise patching can only support devices within its physical support radius, and this limitation alone tips the scale in favor of cloud-based patch management.
Absence of Hardware:
Unlike an on-premise set-up, cloud-based patching does not require any physical servers or databases in the location of operation. This key difference makes cloud-based solutions an attractive option to businesses looking to save costs. Another advantage is the absence of maintenance and its associated cost as well.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Patch Management
Both cloud-based patch management and on-premise patch management tools have their own benefits and drawbacks. While the former is newer and more feature-rich, the latter is much more mature and experienced.
Remote – Infrastructure:
The biggest advantage cloud-based patching has over on-premises patching is support for remote infrastructure. Modern networks consist of workstations throughout the world, and on-premise patching using a patch management tool isn’t possible for all of them. Cloud-based patching can work remotely to ensure a safe and secure network with timely patches and quick remote support.
Hardware Requirements:
Cloud-based patching doesn’t require a physical server or any physical hardware to function since everything is in the cloud. This is both beneficial and detrimental. While the cloud set-up is significantly cheaper, if the cloud set-up fails, we are helpless until the issue is fixed by vendors. But with an on-prem set-up, downtime can be resolved quickly through instant response instead of waiting for the issue to be fixed.
Security of Patching Infrastructure:
With a cloud based set-up, data is exchanged through the internet. This means open ports, firewall exceptions, and more, and this can lead to a security breach. This also requires additional care and monitoring of traffic to detect and respond in case of a cyberattack. But in an on-prem air-gapped network, the chance of a breach occurring is significantly less due to the lack of open ports, etc. That’s also why it’s found in the stock market, the military, etc., where security is critical, and breaches can be devastating.
Ease of adoption:
Since cloud based patch management software does not need any physical hardware, setting it up and running is significantly easier when compared to on-premise patching. This, combined with the wide reach of cloud based patching, is a significant advantage that has led to its adoption over on-premise solutions.
Maintenance and Set-up Costs:
With the lack of hardware requirements, the cost of the set-up of cloud based patching is considerably lesser when compared to an on-prem set-up. On-prem hardware also needs timely maintenance, which leads to additional costs. Cloud based patch management isn’t very cheap. But when compared to on-prem set-ups, the overall cost during the long run is significantly cheaper.
How do you Choose the Best Cloud Based Patch Management Tool?
Lots of factors determine the quality of a tool. A good cloud based patching tool should tick a few boxes that can differentiate it from the rest. Here are some questions you should ask while using it to determine if the tool is good or not.
Is the tool easy to use?
A good cloud based patch management software should have an easy UI and a simple learning curve. With a clean dashboard, the user should efficiently access and use the different features.
What’s the range of support of OSs and devices?
A good patch management tool should support all old versions, servers, and desktops. This helps to have a central console to manage all the devices.
Can it perform automated tasks?
Great patch management tools should support the automation of the patch management process. It should automatically download and deploy the latest patches and ensure the patches are applied correctly.
Cloud Based Patching with SanerNow
SanerNow is a cloud based patching tool that ticks all the right boxes and is a complete solution for all your patching needs.
SanerNow simplifies patch management from a tedious, manual task to a smooth, streamlined process. Every step of the patch management process, be it scanning or deployment or anything in between, can be completely automated through SanerNow.
SanerNow supports all major OSs like Windows, Linux, and macOS and patches a huge array of over 400+ unique third-party applications. And it works on all network devices like workstations, switches, routers, and more.
With SanerNow’s perimeter-less patching, you can patch any and all supported devices without restriction or perimeters, and every step of patch management boils down to a simple click of buttons.
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
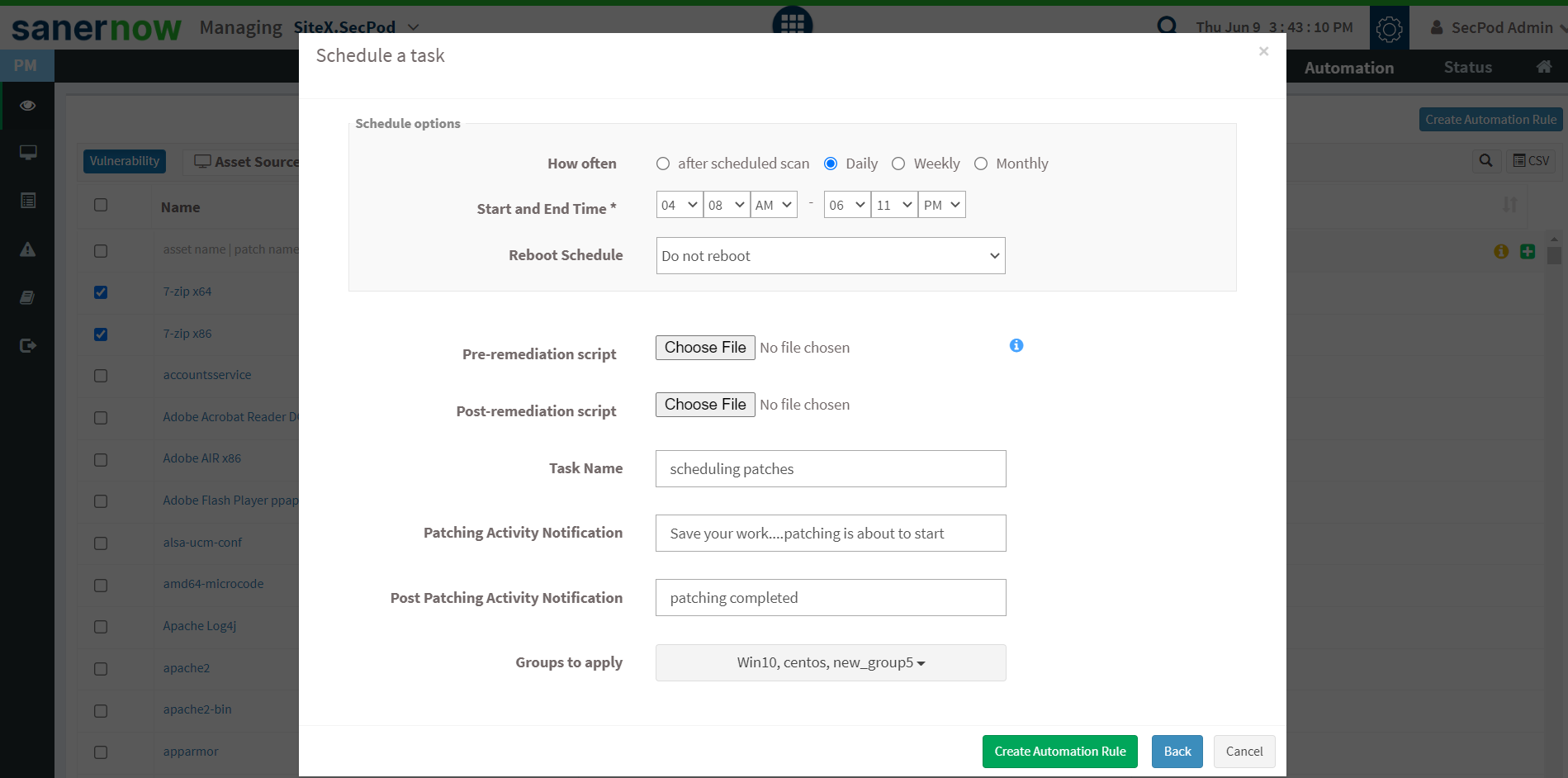
Step 4: