Fox Kitten Campaign has hit the headlines recently, but has a longstanding history of cyber espionage. Researchers from ClearSky discovered a three-year-old campaign targeting a wide range of organizations around the world. In a detailed report, the researchers added that this could be Iran’s most continuous and comprehensive campaign known.
Fox Kitten Campaign, first revealed by Dragos and named Parasite, is known to have strong allies with Advanced Persistent Threat(APT) groups like APT33-Elfin, APT34-OilRig, and APT39-Chafer. The main objective of this campaign is data exfiltration. The campaign has used various tools and techniques to achieve its goals. Using a vulnerability management tool is useful.
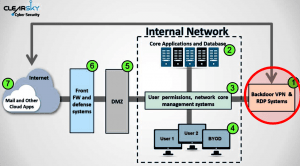
Unpatched VPN and RDP services have been significant targets for this campaign. The Iranian attackers behind this campaign are capable of exploiting vulnerabilities within a few hours or days of their publication. Though not observed before, the infrastructure used in the campaign can be used to deliver destructive malware such as ZeroCleare and Dustman. Patching can be done using a patch management software.
Fox Kitten Campaign : Tools, Techniques and Procedures
1. Tools
Fox Kitten has used a wide variety of tools for initial infection, gaining foothold on the networks, steal confidential information and carry out supply chain attacks.
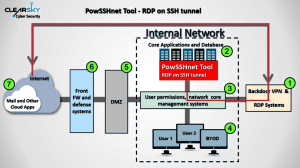
- Custom Tools: The attackers developed tools to suit 32 bit and 64 bit operating systems. A custom backdoor named POWSSHNET was used to maintain secret access to networks via RDP over SSH Tunneling. Other self-developed tools include STSRCheck, VBScript, Socket-based backdoor over cs.exe, Port.exe, etc.
- Open-Source Tools: A few opens-ource tools such as JuicyPotato and Invoke the Hash, were borrowed and modified to fit their requirements.
- Sysadmin Tools: The attackers leveraged legitimate sysadmin software like Putty, Plink, Ngrok, Serveo or FRP to infiltrate corporate networks.
2. Exploitation techniques
Initial Infection
The main attack vector for this campaign is the unpatched flaws in VPN servers. The exploited vulnerabilities are:
- CVE-2019-11510 Pulse Secure
- CVE-2018-13379 Fortinet FortiOS
- CVE-2019-1579 Palo Alto Networks VPN
 Credits: ClearSky Cyber Security
Credits: ClearSky Cyber Security
Exploitation of these vulnerabilities grants attackers the access to targets and their core systems. The attackers download different files, move laterally in the network and try to gain a foothold.
Privilege Escalation and Persistence Mechanisms
After successful infection using VPN vulnerabilities, the attackers try to escalate privileges using a tool named Juicy Potato. The attackers ensure they are not running on virtual environments before taking any step further in the infection chain. The attackers also steal users credentials using ProcDump and Mimikatz. Once they obtain the passwords of the users, attackers abuse the settings of the “sticky keys” accessibility tool to further elevate their privileges. In order to achieve persistence on the target, the attackers create a special local admin user. This allows attackers to maintain high privileges even when the password of the main user on the target changes.
Lateral Movement
The next step in the attack chain is to spread the infection across the network. A range of tools such as STSRCheck, PORT.EXE, Invoke the Hash, POWSSHNET, are used to map servers and open ports, perform specialized scan for servers and predefined ports, and also perform “pass the hash” attacks.
Deployment of Backdoors
POWSSHNET backdoor is installed on targets to open an SSH tunnel. However, after successful installation, the attacker can connect using RDP to the target computer to collect sensitive files.
 Credits: ClearSky Cyber Security
Credits: ClearSky Cyber Security
The attackers also use a tool named “cs.exe” to create another backdoor as an additional communication channel.
Data exfiltration
The attackers behind Fox Kitten Campaign mainly aim at stealing confidential information from targets. However, the campaign has used a plethora of tools to maintain access to the servers inside the targeted organization which helped to establish the foothold in the organization and exfiltrate stolen files. Two kinds of webshells utilize to achieve this. Firstly, place a webshell inside the organization accessible to the network and use another external webshell to upload files. Filter the exfiltrated data and compress into WinRAR or 7-ZIP files and then sent to the attackers.
3. Targets
Fox Kitten Campaign has targeted organizations in Israel, USA, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, Kuwait, UAE, Australia, France, Poland, Germany, Finland, Hungary, Italy and Austria. The sectors include IT, defense, electricity, oil and gas, and then aviation companies.
General Recommendations to prevent security breaches
Organizations must ensure the safety and security of the systems by:
1. Minimizing the exposure of the administration interfaces to the outside world.
2. Regularly updating the systems with released patches.
3. Educating individual users to follow security best practices.
4. Creating two-step authentication mechanisms to reach the corporate core systems.
5. Constant monitoring of active users and user permissions on systems.

