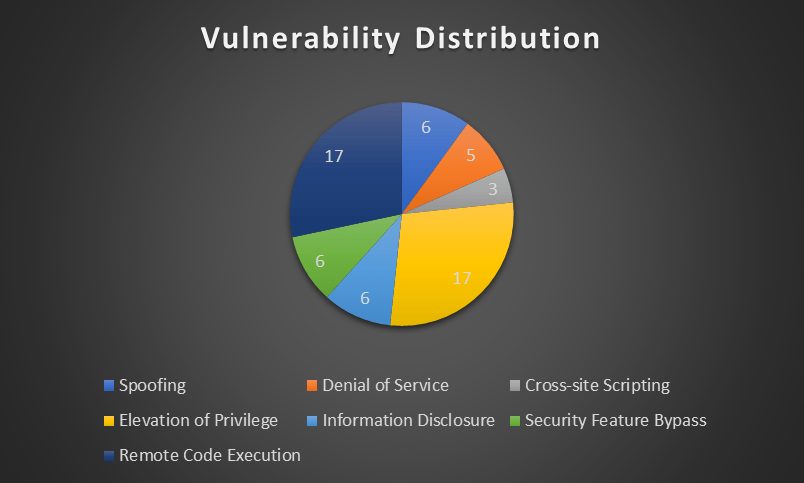
This Patch Tuesday November 2023, Microsoft fixed 75 vulnerabilities, with three rated as critical and 57 rated as important. Elevation of Privilege and Remote Code Execution vulnerabilities are tied for the most common categories at 17 each, with one in each category being critical. The third critical vulnerability is related to Information Disclosure.
Zero Day Vulnerabilities solved by Microsoft Patch Tuesday, November 2023
- CVE-2023-36413 – Microsoft Office, Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability: Exploiting this vulnerability enables an attacker to circumvent the Office Protected View and open a file in editing mode instead of the more secure protected mode. Although to execute this attack, the attacker must send a malicious file to the user and persuade them to open it.
- CVE-2023-36036 – Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver, Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability: A mini-filter driver can filter I/O activities based on I/O Request Packet (IRP) operations, including fast I/O and file system filter (FSFilter) callback actions. Such a driver can register pre and post-operation callback routines for specific I/O operations it intends to filter.
Successful exploitation could thus allow an attacker to gain SYSTEM privileges. - CVE-2023-36038 – ASP.NET Core, Denial of Service Vulnerability: ASP.NET, a widely used web development framework for building web applications on the .NET platform, has an open-source version called ASP.NET Core, which is compatible with Windows, Linux, and macOS. Unlike its predecessors, ASP.NET Core is not exclusive to Windows, marking a framework redesign. This vulnerability can be exploited when HTTP requests to .NET 8 RC 1 are canceled under the IIS InProcess hosting model.
- CVE-2023-36033 – Windows DWM Core Library, Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability: The Desktop Window Manager (DWM) is a fundamental system file in Microsoft Windows, responsible for rendering every visible component on a computer screen. It also manages visual effects like system animations, wallpapers, themes, thumbnails, Windows Aero, Windows Flip, Windows Flip3D, and transparent elements.
Therefore, If successfully exploited, the vulnerability could grant an attacker SYSTEM privilege. - CVE-2023-36025 – Windows SmartScreen, Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability: Windows SmartScreen, a security feature in Microsoft Windows, is a defense against malicious software and websites. It operates in the background, utilizing a cloud-based component to regularly scan web pages for security risks.
To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must certainly persuade a user to click on a specially crafted Internet Shortcut (.URL) or a hyperlink pointing to an Internet Shortcut file. Successful exploitation thus allows attackers to bypass Windows Defender SmartScreen checks and associated prompts.
Three of the fixed zero-day vulnerabilities (namely CVE-2023-36036, CVE-2023-36033, and CVE-2023-36025) were known to be actively exploited in the wild. So, Microsoft November Patch Tuesday helps prevent such exploitation.
Critical Vulnerabilities
- CVE-2023-36052 – Azure CLI REST Command, Information Disclosure Vulnerability: The Azure CLI, a command-line tool facilitating interaction with Microsoft Azure resources, significantly offers a native CLI interface essential for Azure-related tasks. Leveraging the Azure REST API, the Azure CLI executes actions corresponding to each Azure CLI (az) command.
However, This vulnerability could enable an unauthenticated attacker to retrieve plaintext passwords and usernames from log files stored in open-source repositories. - CVE-2023-36400 – Windows HMAC Key Derivation, Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability: The Hash-based Message Authentication Code (HMAC) serves as a mechanism to find out whether a message, transmitted through an insecure channel, has been tampered with when both the sender and receiver possess secret keys. However, This cryptographic authentication technique uses a hash function and a shared secret key to encrypt information, protecting it from unauthorized access.
An attacker must log on to the system and execute a specially crafted application to exploit this vulnerability. If successful, the attacker could potentially gain SYSTEM privileges. - CVE-2023-36397 – Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM), Remote Code Execution Vulnerability: Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) is a multicast computer network transport protocol designed for multi-receiver file transfer applications, ensuring a reliable sequence of packets to multiple recipients concurrently.
In the context of a Windows message queuing service running in a PGM Server environment, an attacker could exploit this vulnerability by transmitting a specially crafted file over the network. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability may grant the attacker the ability to execute remote code and attempt to trigger malicious code.
Products Affected
In this Microsoft November Patch Tuesday, 20+ vulnerabilities were found in Microsoft Edge, making it the most affected product this month. Here is a list of patched products:
- .NET Framework
- ASP.NET
- Azure
- Azure DevOps
- Mariner
- Microsoft Bluetooth Driver
- Microsoft Dynamics
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Sales
- Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based)
- Microsoft Exchange Server
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft Remote Registry Service
- Microsoft WDAC OLE DB provider for SQL
- Microsoft Windows Search Component
- Microsoft Windows Speech
- Open Management Infrastructure
- Tablet Windows User Interface
- Visual Studio
- Visual Studio Code
- Windows Authentication Methods
- Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver
- Windows Common Log File System Driver
- Windows Compressed Folder
- Windows Defender
- Windows Deployment Services
- Windows DHCP Server
- Windows Distributed File System (DFS)
- Windows DWM Core Library
- Windows HMAC Key Derivation
- Windows Hyper-V
- Windows Installer
- Windows Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)
- Windows Kernel
- Windows NTFS
- Windows Protected EAP (PEAP)
- Windows Scripting
- Windows SmartScreen
- Windows Storage
To protect your devices, follow the steps in Microsoft’s security guides for each vulnerability and patch your software.
SanerNow Vulnerability Management, Risk Prioritization, and Patch Management detect and automatically fix vulnerabilities with risk-based remediation. With SanerNow, you can keep your systems updated and secure.

