Microsoft addressed 90 flaws and patched 10 zero-day bugs, of which six are actively exploited in the wild in the August 2024 Patch Tuesday update.
Of the 90 vulnerabilities, 81 belong to the Important category, seven to the Critical category, and one to the Moderate category.
Remediate these critical vulnerabilities immediately with patch management tool.
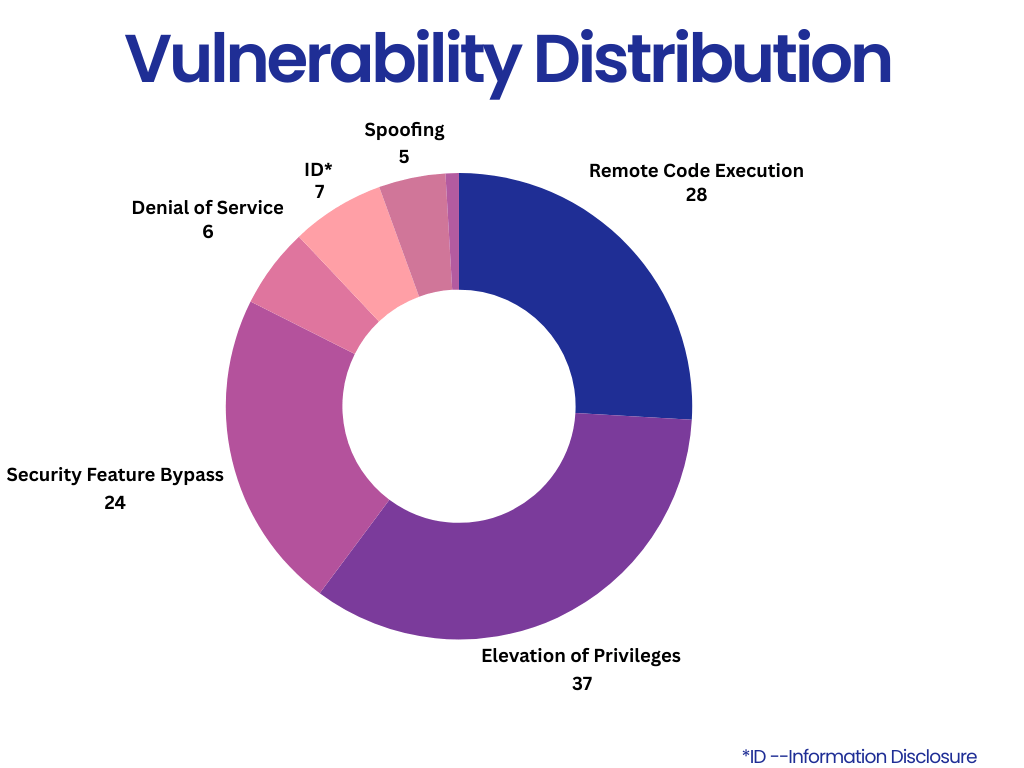
In the August month of Patch Tuesday, the Elevation of Privilege vulnerabilities had a majority share, followed by Remote Code Execution, Information Disclosure, Denial of Service, Security Feature Bypass, Spoofing, and Tampering.
Critical Zero-Click Vulnerability in Windows TCP/IP (CVE-2024-38063)
The recent discovery of a zero-click vulnerability in the Windows TCP/IP stack has raised alarms across the tech industry. This exploit, identified as CVE-2024-38063, allows attackers to execute malicious code on a target machine without the need for the victim to open a file, click a link, or take any other action.
Technical Details
The vulnerability resides in the TCP/IP protocol suite used by Windows operating systems to facilitate network communication. Specifically, it affects the way Windows handles certain network packets, allowing an attacker to send a specially crafted packet to a vulnerable system. This packet triggers a buffer overflow or similar memory corruption, leading to arbitrary code execution on the target machine.
The exploit leverages a flaw in the processing of IP options within the TCP/IP stack. By carefully crafting a packet that includes malicious data in the IP options field, an attacker can exploit this vulnerability to gain control over the affected system. This is particularly concerning for systems connected to the internet or untrusted networks, as they are most likely to receive malicious packets.
Impact
The zero-click vulnerability in the Windows TCP/IP stack poses a severe security threat by enabling attackers to gain full control over systems without user interaction, which can lead to unauthorized access, data theft, and malware deployment, such as ransomware or spyware. The widespread use of Windows systems means this exploit could affect a large number of organizations, highlighting the urgent need for immediate patching and robust network security measures to mitigate these risks.
Mitigation
To mitigate the risk of attack, apply patches immediately and ensure that all Windows systems are updated with the latest security patches from Microsoft.
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Microsoft has patched a total of ten zero-day vulnerabilities in its August edition. Six of the ten vulnerabilities are actively exploited in the public.
The six Actively Exploited Zero-Days are as follows:
CVE-2024-38178 Windows Scripting Engine Memory Corruption Vulnerability
(CVSS Score: 7.5) (Severity: Important) (Vulnerability Type: Remote Code Execution)
This vulnerability affects the Windows Scripting engine, leading to memory corruption and allowing the attacker to execute arbitrary code with the current user’s privileges. The vulnerability requires user interaction and can be exploited over the network. Although the attack vector is network-based, it requires user interaction and has a high attack complexity. The vulnerability’s potential impact is significant as it requires no privileges.
The CVE-2024-38178 is part of the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerability list and is actively being exploited in the wild. Microsoft claims that the CVE-2024-38178 vulnerability as Exploitation Detected.
CVE-2024-38189 Microsoft Project Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
(CVSS Score: 8.8) (Severity: Important) (Vulnerability Type: Remote Code Execution)
This vulnerability affects Microsoft Project, allowing the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the target machine with the same privileges as the Microsoft Project user. For the attacker to successfully exploit the vulnerability, the users must open a malicious MS Office Project file on a system where the Block macros from running in Office files from the Internet policy is disabled, and VBA Macro Notification Settings are not enabled. The attacker can gain unauthorized access to sensitive information by exploiting the vulnerability.
The CVE-2024-38189 is part of the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerability list and is being actively exploited in the wild. Microsoft claims that the CVE-2024-38189 vulnerability as Exploitation Detected.
CVE-2024-38107 Windows Power Dependency Coordinator Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
(CVSS Score: 7.8) (Severity: Important) (Vulnerability Type: Elevation of Privilege)
This vulnerability affects the Windows Power Dependency Coordinator, which is responsible for managing power usage, including waking from sleep mode. An attacker with low privileges could exploit this vulnerability to escalate their privilges to gain complete control of the target system.
Microsoft claims that the CVE-2024-38107 vulnerability as Exploitation Detected.
CVE-2024-38106 Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
(CVSS Score: 7.0) (Severity: Important) (Vulnerability Type: Elevation of Privilege)
This vulnerability affects the Windows Kernel, which grants the attacker SYSTEM-level access upon winning a race condition. The attacker could potentially execute arbitrary code with higher privileges, access sensitive information, and cause potential damage to the system.
The CVE-2024-38106 is part of the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerability list and is actively being exploited in the wild. Microsoft claims that the CVE-2024-38106 vulnerability as Exploitation Detected.
CVE-2024-38213 Windows Mark of the Web Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
(CVSS Score: 6.5) (Severity: Moderate) (Vulnerability Type: Security Feature Bypass)
This vulnerability allows the attacker to bypass the Mark of the Web in Windows, which is used to identify files downloaded from the internet. Windows uses the mark to notify users via SmartScreen that they are about to run a potentially dangerous file. Upon successful exploitation, the attacker can allow malicious files to bypass SmartScreen.
Microsoft claims that the CVE-2024-38123 vulnerability as Exploitation Detected.
CVE-2024-38193 Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability.
(CVSS Score: 7.8) (Severity: Important) (Vulnerability Type: Elevation of Privilege)
This vulnerability affects the Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock. This vulnerability is a local vulnerability with a low attack complexity, needs low privileges to exploit, and requires no user interaction. Upon successful exploitation, this vulnerability could grant system privileges to attackers.
Microsoft claims that the CVE-2024-38193 vulnerability as Exploitation Detected.
The four publicly disclosed vulnerabilities are as follows:
CVE-2024-38199 Windows Line Printer Daemon Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
(CVSS Score: 9.8) (Severity: Important) (Vulnerability Type: Remote Code Execution)
This vulnerability affects the Windows Line Printer Daemon, allowing the attacker to remotely execute code on the target system and gain complete control of the affected system.
Microsoft claims that the CVE-2024-38199 vulnerability as Exploitation Less Likely.
CVE-2024-21302 Windows Secure Kernel Mode Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
(CVSS Score: 6.7) (Severity: Important) (Vulnerability Type: Elevation of Privilege)
This vulnerability affects the Windows Line Printer Daemon, allowing the attacker to remotely execute code on the target system and gain complete control of the affected system.
Microsoft claims that the CVE-2024-21302 vulnerability as Exploitation Less Likely.
CVE-2024-38200 Microsoft Office Spoofing Vulnerability
(CVSS Score: 6.5) (Severity: Important) (Vulnerability Type: Spoofing)
This vulnerability affects Microsoft 365 Apps, Office 2016, Office 2019, and Office Long Term Servicing Channel 2021, which allows attackers to force Office to make an outbound connection to a remote share where attackers could steal sent NTLM hashes.
Microsoft claims that the CVE-2024-38200 vulnerability as Exploitation Less Likely.
CVE-2024-38202 Windows Update Stack Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
(CVSS Score: 7.3) (Severity: Important) (Vulnerability Type: Elevation of Privilege)
This vulnerability exists in the Windows Backup, allowing attackers with basic user privileges to re-introduce previously mitigated vulnerabilities or circumvent some features of Virtualization Based Security (VBS). The attacker must trick or convince an administrator or a user with elevated privileges to perform a system restore that unintentionally triggers the vulnerability.
Microsoft claims that users need not act on the vulnerability as it is only exploitable at run time. The impacted version of WinRE has been replaced with a newer version.
Microsoft claims that the CVE-2024-38202 vulnerability as Exploitation Less Likely.
Microsoft Security Bulletin Summary for August 2024
Microsoft released security updates for the following products in the August Patching Tuesday release.
· .NET and Visual Studio
· Azure Connected Machine Agent
· Azure CycleCloud
· Azure Health Bot
· Azure IoT SDK
· Azure Stack
· Line Printer Daemon Service (LPD)
· Microsoft Bluetooth Driver
· Microsoft Dynamics
· Microsoft Local Security Authority Server (lsasrv)
· Microsoft Office
· Microsoft Office Excel
· Microsoft Office Outlook
· Microsoft Office PowerPoint
· Microsoft Office Project
· Microsoft Office Visio
· Microsoft Streaming Service
· Microsoft Teams
· Microsoft WDAC OLE DB provider for SQL
· Microsoft Windows DNS
· Reliable Multicast Transport Driver (RMCAST)
· Servicing Stack Updates
· Visual Studio
· Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock
· Windows App Installer
· Windows BitLocker
· Windows Clipboard Virtual Channel Extension
· Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver
· Windows Common Log File System Driver
· Windows Compressed Folder
· Windows Deployment Services
· Windows DWM Core Library
· Windows Initial Machine Configuration
· Windows IP Routing Management Snapin
· Windows Kerberos
· Windows Kernel
· Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers
· Windows Layer-2 Bridge Network Driver
· Windows Mark of the Web (MOTW)
· Windows Mobile Broadband
· Windows Network Address Translation (NAT)
· Windows Network Virtualization
· Windows NT OS Kernel
· Windows NTFS
· Windows Power Dependency Coordinator
· Windows Print Spooler Components
· Windows Resource Manager
· Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS)
· Windows Scripting
· Windows Secure Boot
· Windows Secure Kernel Mode
· Windows Security Center
· Windows SmartScreen
· Windows TCP/IP
· Windows Transport Security Layer (TLS)
· Windows Update Stack
· Windows WLAN Auto Config Service
We recommend that you patch these vulnerabilities immediately using SanerNow to secure your devices and prevent attacks on your organization.

