September’s coming in hot! Out of the 79 vulnerabilities it has under its belt, 4 are zero-days, and each zero-day is known to have been actively exploited. Luckily, Microsoft has saved us from impending calamity once more and released patches for them all.
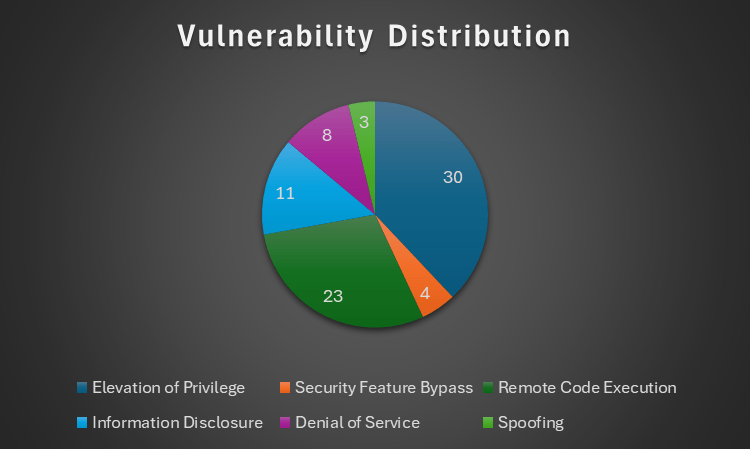
The most popular vulnerability category this month is Elevation of Privilege, which spans a whopping 30 of the 79 vulnerabilities patched. Remote Code Execution is a close second at 23. The chart below offers more details regarding September’s vulnerability distribution.
You can detect and remediate such critical vulnerabilities instantly with a patch management tool.
Zero Day Vulnerabilities
CVE-2024-38217: Windows Mark of the Web, Security Feature Bypass, CVSS 5.4 – This publicly disclosed vulnerability follows a technique known as “LNK stomping,” where exploitation typically occurs when explorer.exe overwrites an existing LNK file. Exploit code is available on GitHub, and the discoverer references VirusTotal samples dating back to 2018, suggesting long-standing abuse of this vulnerability.
Like other MotW bypass vulnerabilities, this one is exploited when a user downloads and opens a specially crafted malicious file, which allows it to bypass SmartScreen’s Application Reputation checks or the legacy Windows Attachment Services security prompts.
CVE-2024-43491: Microsoft Windows Update, Remote Code Execution, CVSS 9.8 – This flaw in the Servicing Stack effectively reverses previous fixes and mitigations, rendering earlier security patches ineffective. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities that were previously addressed on Windows 10 version 1507 systems that have installed the Windows security update KB5035858 or other updates released up to August 2024.
This issue, however, only affects Windows 10 Enterprise 2015 LTSB and Windows 10 IoT Enterprise 2015 LTSB, and later versions of Windows 10 are not impacted.
CVE-2024-38014: Windows Installer, Elevation of Privilege, CVSS 7.8 – Exploiting this vulnerability allows code execution with SYSTEM privileges. Although the attack vector is local, it could still appeal to malware authors due to its low complexity, minimal privilege requirements, and lack of user interaction.
This scenario likely falls under CWE-269: Improper Privilege Management, where the Windows Installer may grant excessive privileged access while installing software or configuring the operating system.
CVE-2024-38226: Microsoft Publisher, Security Feature Bypass, CVSS 7.3 – An attacker with authentication could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a web visitor to download and open a specifically crafted file from a website. If executed, the attacker could circumvent Office macro policies meant to block untrusted or malicious files.
This local attack relies on social engineering to convince the victim to engage with the malicious file on their own device, potentially leading to a security breach.
Other Notable Flaws addressed in September 2024 Patch Tuesday
Aside from the zero days, a few critical vulnerabilities were patched. The table below provides some details about them.
| CVE | CVSS Score | Description |
| CVE-2024-38220 | 9.0 | Azure Stack Hub Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38018 | 8.8 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38194 | 8.4 | Azure Web Apps Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38216 | 8.2 | Azure Stack Hub Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38119 | 7.5 | Windows Network Address Translation (NAT) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-43464 | 7.2 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |

Products Affected
- Azure CycleCloud
- Azure Network Watcher
- Azure Stack
- Azure Web Apps
- Dynamics Business Central
- Microsoft AutoUpdate (MAU)
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 (on-premises)
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Management Console
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office Publisher
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft Office Visio
- Microsoft Outlook for iOS
- Microsoft Streaming Service
- Power Automate
- Role: Windows Hyper-V
- SQL Server
- Windows Admin Center
- Windows AllJoyn API
- Windows Authentication Methods
- Windows DHCP Server
- Windows Installer
- Windows Kerberos
- Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers
- Windows Libarchive
- Windows Mark of the Web (MOTW)
- Windows MSHTML Platform
- Windows Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Windows Network Virtualization
- Windows PowerShell
- Windows Remote Access Connection Manager
- Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service
- Windows Security Zone Mapping
- Windows Setup and Deployment
- Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service
- Windows Storage
- Windows TCP/IP
- Windows Update
- Windows Win32K – GRFX
- Windows Win32K – ICOMP
If you’re using any of these products, you should patch them immediately! Microsoft’s Security Update Guide details mitigations and patches for each vulnerability. You can also use tools to help you apply those patches.
Instantly Fix Risks with SanerNow Patch Management
SanerNow patch management is a continuous, automated, and integrated software that instantly fixes risks exploited in the wild. The software supports major operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS, as well as 550+ third-party applications.
It also allows you to set up a safe testing area to test patches before deploying them in a primary production environment. SanerNow patch management additionally supports a patch rollback feature in case of patch failure or a system malfunction.
Experience the fastest and most accurate patching software here.


