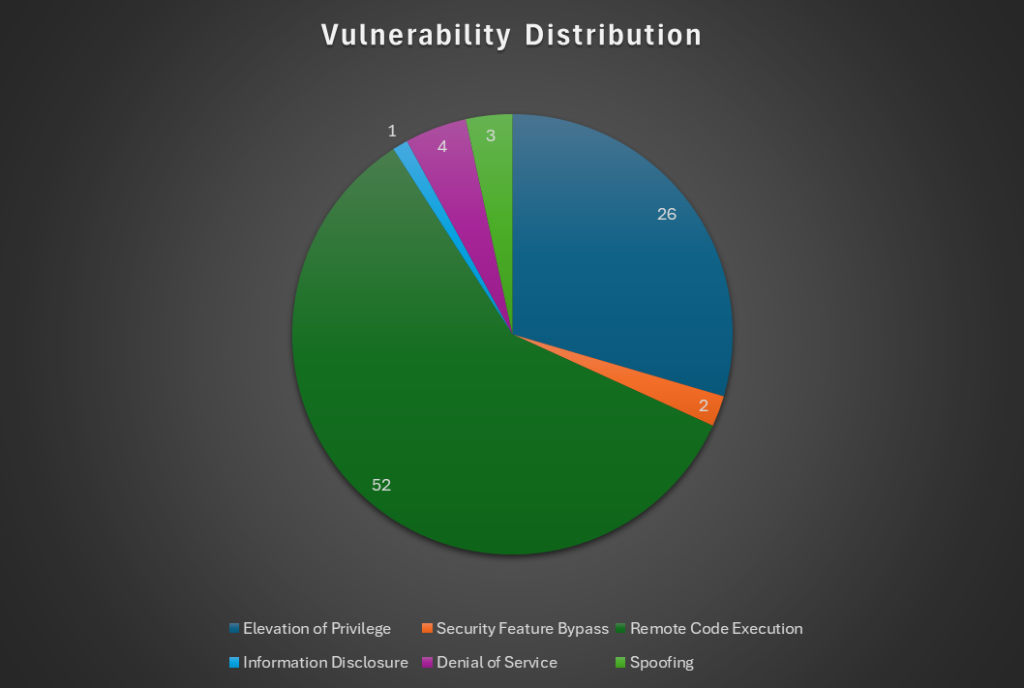
This month, Microsoft released security updates addressing 88 vulnerabilities, four of which were zero-days and four critical. Two of the zero-days are known to have been actively exploited, and three have been publicly disclosed. The chart below offers some insight into the types of vulnerabilities found.
You can detect and remediate such vulnerabilities instantly with a patch management tool.
Zero Day Vulnerabilities
The following two flaws were actively exploited.
CVE-2024-43451: Microsoft Windows, NTLM Hash Disclosure Spoofing, CVSS 6.5—Malicious files can expose users’ NTLMv2 hashes to remote attackers with minimal, single-click user interaction. Attackers can then use a said hash to authenticate as the user. This vulnerability was publicly disclosed.
CVE-2024-49039: Windows Task Scheduler, Elevation of Privilege, CVSS 8.8 – By starting an attack from a low-privilege AppContainer, an attacker can elevate their privilege to the Medium Integrity level, which allows them to execute RPC functions that are usually only available to privileged accounts.
The following two flaws were publicly disclosed but not actively exploited.
CVE-2024-49040: Microsoft Exchange Server, Spoofing, CVSS 7.5 – The P2 FROM header verification process in Microsoft Exchange Server is flawed, allowing attackers to spoof email sender addresses when sending messages to local recipients.
Microsoft now detects and flags spoofed emails by sending an email body alert: “Notice: This email appears to be suspicious. Do not trust this email’s information, links, or attachments without verifying the source through a trusted method.”
CVE-2024-49019: Active Directory Certificate Services, Elevation of Privilege, CVSS 7.8 – With default version 1 certificate templates, an attacker can craft a CSR that includes application policies that override the Extended Key Usage attributes specified in the template. The only requirement is enrollment rights, which then allow the generation of client authentication, certificate request agent, and code-signing certificates using the Web Server template. This can result in attackers escalating their privileges to those of domain administrators.
Products Affected
- .NET and Visual Studio
- Airlift.microsoft.com
- Azure CycleCloud
- LightGBM
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based)
- Microsoft Exchange Server
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office SharePoint ADV240001 Microsoft SharePoint Server Defense in Depth Update None
- Microsoft Office Word
- Microsoft PC Manager
- Microsoft Virtual Hard Drive
- Microsoft Windows DNS
- Windows Active Directory Certificate Services
- Windows Hyper-V
- SQL Server
- TorchGeo
- Visual Studio
- Visual Studio Code
- Windows CSC Service
- Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC)
- Windows DWM Core Library
- Windows Kerberos
- Windows Kernel
- Windows NT OS Kernel
- Windows NTLM
- Windows Package Library Manager
- Windows Registry
- Windows Secure Kernel Mode
- Windows SMB
- Windows SMBv3 Client/Server
- Windows Task Scheduler
- Windows Telephony Service
- Windows Update Stack
- Windows USB Video Driver
- Windows VMSwitch
- Windows Win32 Kernel Subsystem
If you’re using any of these products, you should patch them immediately! Microsoft’s Security Update Guide details mitigations and patches for each vulnerability. You can also use tools to help you apply those patches.
Instantly Fix Risks with SanerNow Patch Management
SanerNow patch management is a continuous, automated, and integrated software that instantly fixes risks exploited in the wild. The software supports major operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS, as well as 550+ third-party applications.
It also allows you to set up a safe testing area to test patches before deploying them in a primary production environment. SanerNow patch management additionally supports a patch rollback feature in case of patch failure or a system malfunction.
Experience the fastest and most accurate patching software here.

