The high severity zero-day vulnerabilities found in Cisco IOS XR – An Internetwork Operating System (IOS) that shipped with Cisco’s networking equipment. The vulnerabilities allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to exhaust process memory. And crash the other processes running on the affected device. A vulnerability management solution can stop these vulnerabilities from attacking.
Vulnerabilities Details (CVE-2020-3566 and CVE-2020-3569):
Cisco has released a security advisory and warned of an actively exploited zero-day vulnerabilities in the Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) feature of Cisco IOS XR Software that installed on carrier-grade and data center routers according to Cisco. This release is nothing but a patch to these vulnerabilities using a patch management tool.
According to Cisco’s advisory: “The vulnerabilities are due to insufficient queue management for Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) packets. An attacker could exploit the vulnerabilities by sending crafted IGMP traffic to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause memory exhaustion, resulting in instability of other processes. These processes may include, but are not limited to, interior and exterior routing protocols.”
The vulnerabilities could affect any Cisco device that is running any release of Cisco IOS XR Software along with multicast routing enabled for an active interface.
Check if Multicast routing is enabled:
An administrator can determine if multicast routing enabled on the device by using “show igmp interface” command. Multicast routing is not enabled if the output of the command is empty. If the output of the command is as follows then multicast routing enabled on the device.

Check if Device Is Receiving DVMRP Traffic:
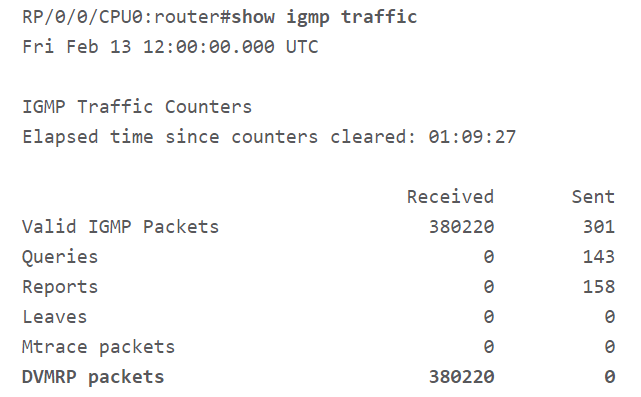
An administrator can determine if the device is receiving DVMRP traffic by using “show igmp traffic” command. From the following image, if the Received column of DVMRP packets entry contains a value of zero and if it continues to remain zero even on subsequent executions of the command, then the device is not receiving DVMRP traffic.
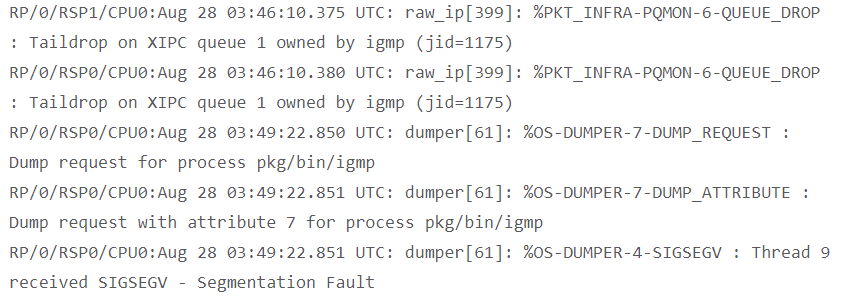
Indicators of Compromise:
The following entries may in the system logs when a device compromises.
Impact:
The vulnerabilities allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to exhaust process memory and crash the other processes running on the affected device.
Affected Application:
The vulnerabilities affect all versions of Cisco IOS XR Software installed on any Cisco device, with multicast routing enabled for an active interface.
Mitigations:
1. IGMP traffic rate limiter:
An Administrator can use lpts pifib hardware police flow igmp rate command to limit the traffic rate against the current average traffic rate. This command will not remove the vector needed for exploitation but it will reduce the traffic rate and increase the time necessary for exploitation which in turn will give more time to the administrator to perform recovery actions.
lpts pifib hardware police flow igmp rate <value>
2. access control entry (ACE) or access control list (ACL)
An Administrator can create ACE to an existing ACL or create a new ACL for a specific interface that denies DVMRP traffic inbound on that interface. Uses the following command to implement an ACL
ipv4 access-list <acl_name> deny igmp any any dvmrp
Solutions:
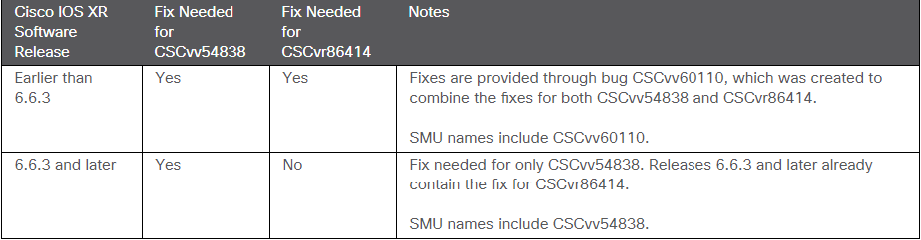
Cisco has released Software Maintenance Upgrades (SMUs) to address these vulnerabilities.