A medium severity zero-day vulnerability has been found in the health check RPM of Cisco IOS XR – An Internetwork Operating System (IOS) that is shipped with Cisco’s networking equipment. This vulnerability (CVE-2022-20821) allows an unauthenticated, remote attacker to access the Redis instance running within the NOSi container. We have cracked this vulnerability using a vulnerability management tool and assigned it CVE-2022-20821, with a CVSS score of 6.5. Cisco issued an advisory for this vulnerability on Friday.
Cisco’s advisory says, “This vulnerability exists because the health check RPM opens TCP port 6379 by default upon activation. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by connecting to the Redis instance on the open port. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to write to the Redis in-memory database, write arbitrary files to the container filesystem, and retrieve information about the Redis database. Given the configuration of the sandboxed container that the Redis instance runs in, a remote attacker would be unable to execute remote code or abuse the integrity of the Cisco IOS XR Software host system.” Also, a reliable patch management tool can patch these vulnerabilities.
Affected Products In Cisco Zero Day Vulnerability:
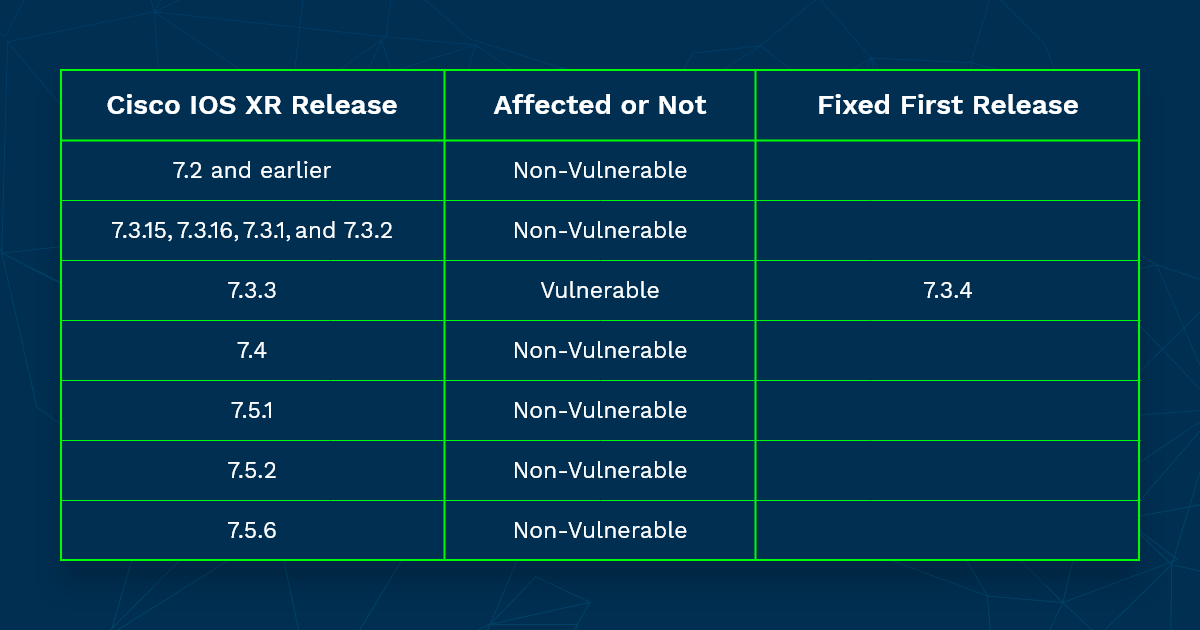
This vulnerability CVE-2022-20821 affects Cisco 8000 Series Routers running on the 7.3.3 version of Cisco IOS XR Software and installing the health check RPM.
Checking if the vulnerable version is installed:
The user can identify if they are affected by running the “run docker ps” CLI command. The device is affected if the output contains the name ‘NOSi.’
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000#run docker ps Wed May 18 04:54:52.502 UTC CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 54307e434f29 nosi:latest "docker-entrypoint.s…" 9 seconds ago Up 8 seconds NOSi RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000#
Credit: Cisco advisory
Mitigations To Cisco Zero Day Vulnerability:
Currently, Cisco provides two workarounds for this vulnerability, listed below:
Option 1:- This is the preferred method by Cisco. By disabling health check and explicitly disabling the use-cases.
To effectively disable the health check, enter the following commands exactly as shown:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000(config)#no healthcheck enable RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000(config)#healthcheck use-case asic-reset disable RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000(config)#healthcheck use-case packet-drop disable RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000(config)#commit RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000#
Credit: Cisco advisory
Then remove the health check RPM from the device:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000#install package remove xr-healthcheck Wed May 18 05:00:08.060 UTCInstall remove operation 5.2.2 has started Install operation will continue in the background RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000# RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000#install apply restart Wed May 18 05:01:08.842 UTC Install apply operation 5.2 has started Install operation will continue in the background RP/0/RP0/CPU0:8000#
Credit: Cisco advisory
Option 2:– By blocking 6379, using an Infrastructure Access Control List (iACLs).
The iACL blocks all the unauthorized Redis communication packets on TCP port 6379, allowing only authorized devices. However, the attack can occur through an authorized Redis communication packet(Trusted sources). Apply the iACLs to all source-to-destination interfaces for the configured IP. The user should first give access to required traffic for routing and administrative access before denying the unauthorized traffic.
ipv4 access-list Infrastructure-ACL-Policy ! !-- The following vulnerability-specific access control entries !-- (ACEs) can drop Redis Database communication packets ! deny tcp any 192.168.60.0 0.0.0.255 eq 6379 ! !-- Explicit deny ACE for traffic sent to addresses configured !-- within the infrastructure address space ! deny ip any 192.168.60.0 0.0.0.255 ! !-- Permit or deny all other Layer 3 and Layer 4 traffic in !-- accordance with existing security policies and configurations ! !-- Apply iACL to interfaces in the ingress direction ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ipv4 access-group Infrastructure-ACL-Policy in
Credit: Cisco advisory
Solution to Cisco Zero Day Vulnerability
Cisco has planned software maintenance upgrades (SMUs) for 7.3.3.
SanerNow has published security content to detect this vulnerability. Cisco said it will release a patch to address the flaw but has not published a timeline. However, we strongly recommend that you apply the mitigations provided by Cisco and follow security best practices until the patch becomes available.