One of the major and serious threats on the internet today is malicious software, often called Malware. Malware, a short form of malicious software, is any software that disrupts computer operations, gathers sensitive information, gains access to private computer systems, or displays irrelevant advertising. The malware is design by attackers as polymorphic and metamorphic, which can change their code as they propagate. The variants of malware families share typical behavioral patterns reflecting their origin and purpose. One of them is Cryptolocker Ransomware. Vulnerability Management Software can prevent these attacks.
Ransomware is a type of malware that employs asymmetric encryption to take a victim’s information hostage over a ransom. Asymmetric (which has public and private) encryption is cryptography in which a pair of keys is used to encrypt and decrypt a file. The attacker uniquely generates the public-private pair of keys for the victim with the private key to decrypt the files stored on the attacker’s server. The attacker makes the private key available to the victim only after paying the ransom. Though that is not always the case, as seen in recent ransomware campaigns. Without access to the private key, it is next to impossible to decrypt the files that are there as ransom. A good Vulnerability management tool can solve these issues.
Background
CryptoLocker is a ransomware which targets computers running Microsoft Windows, believed to have first been posted to the Internet on 5 September 2013. CryptoLocker is propagated via infected email attachments, and via an Exploit kit(EK). Previously the attackers using Angler EK to distribute CryptoLocker is now moved to Neutrino EK. Neutrino Exploit Kit is a malicious code present on fraudulent websites or illegally injected on legitimate but hacked websites without the knowledge of the administrator. The intention behind these code injections is to detect and exploit vulnerabilities on applications installed on your computer to install malicious and unwanted software that compromise the security.
When activated, the ransomware encrypts certain types of files stored on local and mounted network drives using RSA public-key cryptography, with the private key stored only on server controlled by attacker. The ransomware pops up a message, which offers to decrypt the data if a ransom (through either bitcoin or a pre-paid cash voucher) is paid in a stated deadline, and threatened to delete the private key if ransom is not paid before the deadline. If victim does not pay ransom the attacker will delete the private key. In some case the attacker offer to decrypt data via an online service for a significantly higher price in bitcoin (current 1 bitcoin = INR 40335.59 | 604.93 US Dollar).
Infection method
CryptoLocker uses multiple strategies to gain access to the victim’s system. Vulnerabilities in software applications provide an easy route for infecting systems with CryptoLocker. Many exploit kits include ransomware and are actively used to attack systems. Exploit kits are a type of malicious toolkit used to exploit security holes or vulnerabilities found in software applications (Java, Adobe Reader, Adobe Flash etc). These kits come with pre-written exploit code and target users running insecure or outdated software applications on their computers. Ransomware can also enter the system through lack of strict compliance rules within an organization. For example, not preventing auto-run option of USB drives can easily be exploited by perpetrators to execute Ransomware.
Another common strategy adopted by ransomware to gain access to systems via the e-mail. CryptoLocker Ransomware was distributed through spam emails targeting business professionals. 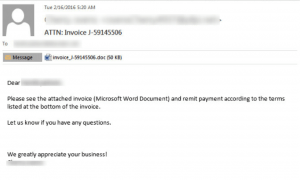 The temptation was often a “consumer complaint” against the email recipient or their organization. Or an invoice of the purchase the victim which has never made, or a mail regarding salary hike from an HR. Attached to these emails was a ZIP archive with a random alphabetical filename containing 13 to 17 characters. Only the first character of the filename is capitalized. The archive contained a single executable with the same filename as the ZIP archive but with an EXE extension.
The temptation was often a “consumer complaint” against the email recipient or their organization. Or an invoice of the purchase the victim which has never made, or a mail regarding salary hike from an HR. Attached to these emails was a ZIP archive with a random alphabetical filename containing 13 to 17 characters. Only the first character of the filename is capitalized. The archive contained a single executable with the same filename as the ZIP archive but with an EXE extension.
Compressed archive,
Jcgnbunudberrr.zip
Lmpjxmvheortt.zip
Icmcobxksjghdlnnt.zip
Gfaiqhgtqakbxlbf.zip
**Note : The file names will be random
Execution and persistence
CryptoLocker hides its presence from victims until it has successfully contacted a command and control (C & C) server and encrypted the files located on connected drives. Before these actions, the malware ensures that it remains running on infected systems and persists across reboots. When first executed, the malware creates a copy of itself in either %AppData% or %LocalAppData%. CryptoLocker then deletes the original executable file.
%APPDATA%\Roaming\{random GUID}.exe,
for example
%APPDATA%\Roaming\{1400BEBE-1503-1236-2800-383F060F181A}.exe.
CryptoLocker then creates an “autorun” registry key:
HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run “CryptoLocker”:<random>.exe
The “Run” registry key is there to run EVERY time that specific user logs in in HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU). It’s like an autoexec.bat or .profile for the machine or user.
Some versions of CryptoLocker create an additional registry entry:
HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce “*CryptoLocker”:<random>.exe
The “RunOnce” registry key under HKCU is there to run ONCE when that user logs in and then the OS will remove it from the registry.
The asterisk at the beginning of the key name ensures that the malware executes even if the system is restarted in “safe mode.”
Additional configuration data is stored in the following registry key:
HKCU\SOFTWARE\CryptoLocker or HKCU\SOFTWARE\CryptoLocker_0388
The VersionInfo value stored within this key contains configuration data encoded with the XOR key 0x819C33AE. The PublicKey value contains the RSA public key received from the C&C server (command and control server) during the initial network connection.
The executable files in early CryptoLocker samples used a random filename formatted like a GUID:
{71257279-042B-371D-A1D3-FBF8D2FADFFA}.exe
Encryption
On execution, CryptoLocker begins to scan mapped network drives that the host is connected (see affected file types), and then it renames and encrypts files and documents which has permission to modify by logged-in user. CryptoLocker uses an RSA 2048-bit key to encrypt the files and renames the files with an extension, such as, .encrypted or .cryptolocker or .[7-8 random characters], depending on the CryptoLocker variant. Finally, the malware creates a file in each infected directory linking to a web page with decryption instructions that require the user to pay ransom in terms of bitcoin. Instruction file names are typically DECRYPT_INSTRUCTION.txt or DECRYPT_INSTRUCTIONS.html.
For instance, CryptoLocker malware creates an EXE file and executes to encrypt all personal data. CryptoLocker uses strong third-party certified cryptography offered by Microsoft’s “CryptoAPI”. By using a sound implementation and following best practices, the malware authors have created a robust program that is difficult to bypass. The malware uses the “Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider” (MS_ENH_RSA_AES_PROV) to create keys and to encrypt data with the RSA (CALG_RSA_KEYX) and AES (CALG_AES_256) algorithms.
The Process:
The encryption process begins after CryptoLocker has recognized its presence on the system and successfully located, connected to, and linked with an attacker-controlled C&C server. This communication offers the malware with the threat actors’ RSA public key, which is in use during the course of the encryption process.
The malware begins the encryption process by using the GetLogicalDrives() API call to enumerate the disks on the system that have been assigned a drive letter (e.g., C:). CryptoLocker samples, the GetDriveType() API call determines if the drives are local fixed disks or network drives (DRIVE_FIXED and DRIVE_REMOTE, respectively). Only those two types of drives are selected for file encryption in early samples. Samples also select removable drives (DRIVE_REMOVABLE), including USB thumb drives and external hard disks.
After selecting a list of disks to attack, the malware considers for encryption of all the files on those disks that match the 72 file patterns shown in the list below.
*.odt, *.ods, *.odp, *.odm, *.odc, *.odb, *.doc, *.docx, *.docm, *.wps, *.xls, *.xlsx, *.xlsm, *.xlsb, *.xlk, *.ppt, *.pptx, *.pptm, *.mdb, *.accdb, *.pst, *.dwg, *.dxf, *.dxg, *.wpd, *.rtf, *.wb2, *.mdf, *.dbf, *.psd, *.pdd, *.pdf, *.eps, *.ai, *.indd, *.cdr, *.jpg, *.jpe, *.jpg, *.dng, *.3fr, *.arw, *.srf, *.sr2, *.bay, *.crw, *.cr2, *.dcr, *.kdc, *.erf, *.mef, *.mrw, *.nef, *.nrw, *.orf, *.raf, *.raw, *.rwl, *.rw2, *.r3d, *.ptx, *.pef, *.srw, *.x3f, *.der, *.cer, *.crt, *.pem, *.pfx, *.p12, *.p7b, *.p7c.
All the files have an encryption with a unique AES key, which in turn is with the RSA public key receiving from the C&C server. The encryption key, metadata, and the encryption file contents are then written back to disk, replacing the original file. Encryption files can only be in recovery by obtaining the RSA private key held exclusively by the threat actors.
Bookkeeping:
As a form of bookkeeping, the malware stores the location of every encrypted file in the following registry key HKCU\SOFTWARE\CryptoLocker(or CryptoLocker_0388)
After completing the file encryption process, CryptoLocker re-scans the system regularly for new drives and files to encrypt.
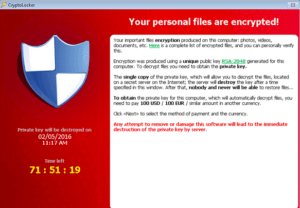
The malware does not disclose its presence to the victim until all targeted files are in encryption. Once all the files are encrypt CryptoLocker pops up with a splash screen containing instructions and an ominous countdown timer for a victim (as shown in the above picture).
It prevents you from accessing your desktop.
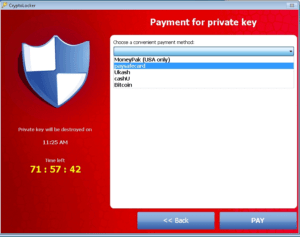
As part of its payload, this threat displays a full-screen web page that covers all other windows, rendering your PC unusable. The warning asks you to pay a ransom to receive a randomly-generated key that will “unlock” your files and let you regain access to your PC. The ransomware displays a countdown clock counting down from 72 hours and gives you the following payment options to pay the ransom:
Bitcoin
cashU
MoneyPak
Paysafecard
Ukash
The key that “unlocks” your PC is unique; you cannot use anyone else’s key. Note that these online payment systems are not in association with this threat in any way.
Victims
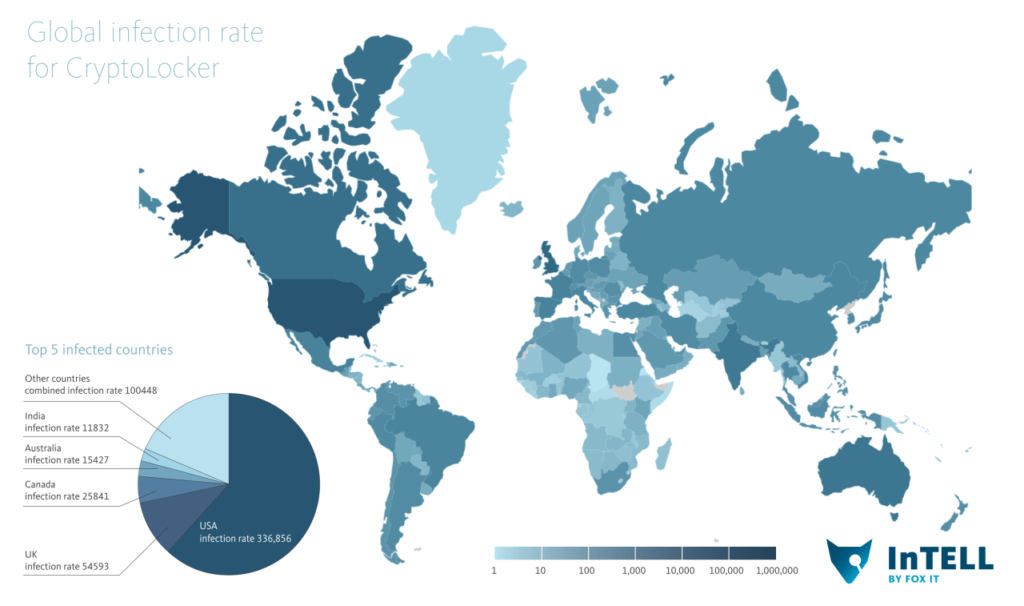 (image credits: www.fox-it.com)
(image credits: www.fox-it.com)
Based on its design, deployment method, and empirical observations of its distribution, CryptoLocker appears to target English speakers, specifically those located in the United States. Malware authors are from Russia and Eastern Europe, whereas the CryptoLocker authors are originating, and commonly target victims in North America and Western Europe. Numerous factors complicate law enforcement cooperation between these regions, which often results in threat actors believing that they can operate with impunity.
Early infections occurred disproportionately at financial institutions, but untrustworthy reports suggest that early victims were in upright as diverse as hospitality and public utilities. There is no evidence the actors are targeting specific industries. The threat actors have also expanded their attacks to include home Internet users and professionals.
Solution
SecPod Saner provides continuous visibility and control of all endpoints. It proactively remediates risks and detects and responds to threats. Saner combines endpoint vulnerability, patch, and compliance management with endpoint threat detection and response into one easy-to-manage solution. Saner helps to detect this kind of dangerous ransomware and Isolate the infected systems from creating more damage to the network drives connected to the affected computer.
How Does Saner Prevent and Detect Ransomware/ Cryptolocker Ransomware?
Prevention
Saner’s first level of defense is prevention. Saner remediates endpoint systems to remove all known vulnerabilities. Removal of vulnerabilities effectively blocks the ability of ransomware to exploit known vulnerabilities. Since known vulnerabilities provide a major gateway, this substantially reduces the entry point and opportunity for ransomware attacks.
Often ransomware use lacks compliance with strict hardening rules to attack endpoint systems. Saner’s compliance management component ensures that endpoint systems are hard and compliant with defined policies. Deviations are monitoring and correcting in real-time. This further reduces the risk of ransomware by eliminating potentially easy paths through which ransomware can enter the system.
Cryptolocker Ransomware Detection
Often ransomware enters systems as an attachment to an email or through a phishing attack or waterhole attack through exploit kits. The user clicks the attachment — which triggers the ransomware attack. The attachment is usually innocuous-looking – made to appear as a genuine artifact from a company or somebody he or she corresponds with regularly. However, the attachment is actually an executable that launches the ransomware.
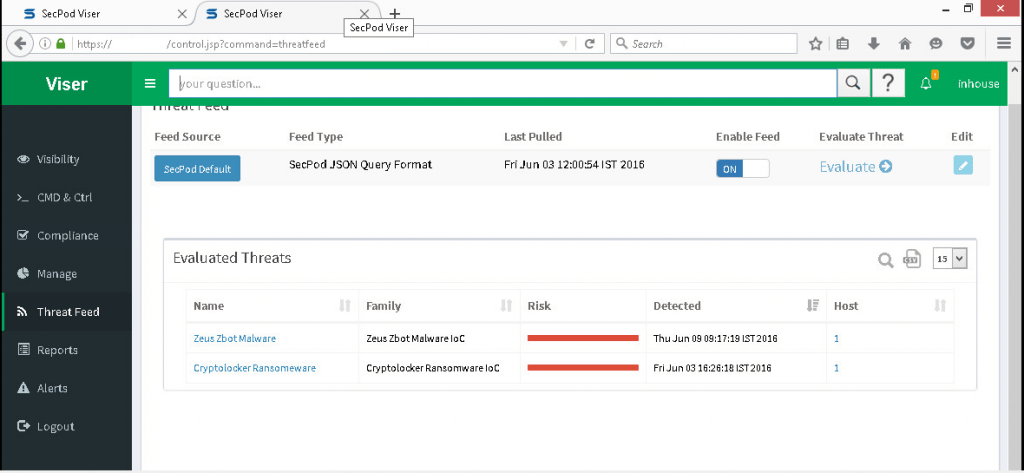
When ransomware enters a system through this channel, detecting the launch immediately is of utmost importance. Saner detects ransomware using an up-to-date threat intelligence database that contains the latest ransomware threat feed. If an attacker successfully gets through with an email attachment, Saner uses the threat feed to detect the ransomware.
In addition to threat intelligence, Saner uses known behavioral patterns of ransomware to detect an ongoing attack. Such behavior includes connecting to a server to procure the key for encryption, modifying certain registry keys, and creating new ones. Additionally, if the attack is in progress, many files with specific extensions are updating. Some variants create files with a new extension. For example, Locky ransomware creates files with an extension .locky. Saner detects these events in real-time.
With this multipronged approach, Saner reduces the risk of ransomware infecting a system or multiple systems connected to a network and helps contain the damage.
Cryptolocker ransomware threat indicators
Saner detects malware on the basis of MD5, registry entries, files, processes, and network connections. Many other artifacts creating by the malware are in use to detect malware in real-time and alert the admin to take action.
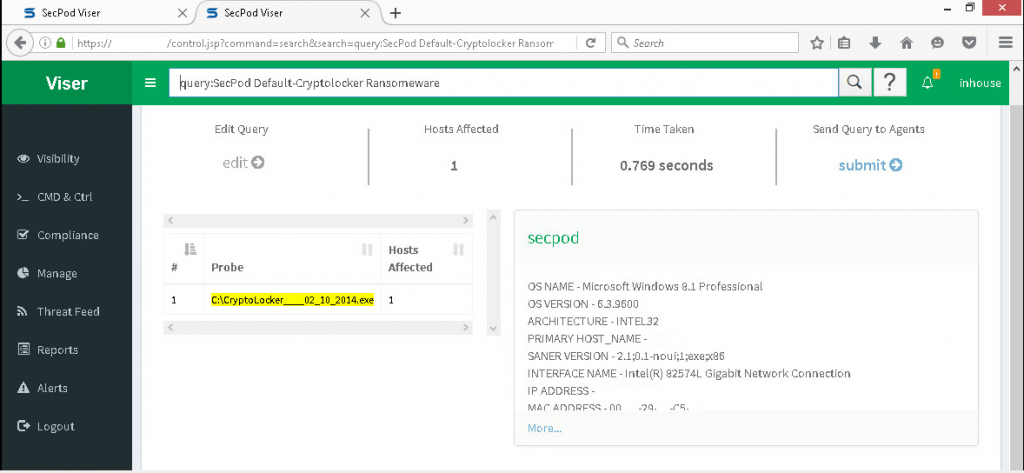
Once the crypto locker executes, it creates the following IoCs.
C:\CryptoLocker____02_10_2014.exe
C:\User.\AppData\Roaming\userinit.exe
C:\User.\AppData\Roaming\msunet.exe
C:\CryptoLocker____02_10_2014.exe
The IoCs (Indicator of Compromise) are capturing by the Saner using Real-Time Monitor, and the Saner uploads the result to the Server. On the basis of the Threat feed, the Saner will evaluate the uploading IoCs and display matching IoCs in the Viser screen, stating that the system is present with CryptoLocker Ransomware.
With this approach, Saner detects an ongoing attack in real-time and considerably reduces the risk of CryptoLocker ransomware infecting a system or other systems in the network and containing the damage. Once the admin sees the ongoing attack, the admin can take appropriate actions by using the C&C section in Viser.
For the new variants of CryptoLocker, this detection strategy may not work and CryptoLocker may launch and execute. When this happens, the damage caused by ransomware can go beyond the system. CryptoLocker Ransomware can wreak havoc by encrypting not only the files on the user’s disk but can encrypt files in the network drives connected to the system.
Solution
Saner provides an admin interface, Viser. The admin is quickly alerting to an ongoing ransomware attack and can take appropriate actions using the C&C section in Viser. Also, the admin can isolate the compromised system and prevent greater damage by isolating the system. Before the ransomware can encrypt the contents of the network file systems. This will significantly reduce the damage ransomware could cause by encrypting files on the network drives connected to the affected computer.
It will become more than a billion dollars a year in crime 2016. Ransomware can attack systems using vulnerabilities, weak configurations, non-compliant systems, and phishing attacks. The damage caused by ransomware can be considerable.
Today ransomware is a sophisticated weapon cybercriminals use.Affecting users in many regions worldwide, targeting those living in developed and high-tech countries. While complete ransomware prevention may not be possible today, Saner helps considerably reduce the risk of ransomware attacks. Further, with its admin console, Saner can reduce the potential damage resulting from ransomware. We are aggressively improving the capability of Saner to handle such threats as ransomware.
“Saner’s first level of defense is prevention” Saner detects all potential vulnerabilities and patches all known vulnerabilities in that system and reduces the entry point and opportunity for cryptolocker or such ransomware attacks.