On Oct 10, 2017, Microsoft announced they would be ending the support for Microsoft Office 2007 ( presently outdated systems) . It was one of the popular suites developed by Microsoft; as per the developers, every Microsoft product will have a support lifecycle during which all updates, patches, and new features will be provided. This support lifecycle would typically be for ten years.
Even though the Microsoft 2007 suite was released decades ago, there are still organizations and individuals using this suite of applications today. However, it’s important to note that Microsoft no longer provides security updates, patches, or technical support.
The lack of ongoing support means that any vulnerabilities or security flaws discovered in Microsoft Office 2007 are not addressed by official updates resulting in lack of remediation by patch management tools. This leaves the software more susceptible to potential security breaches and attacks. Cybercriminals frequently target outdated and unsupported software versions like Office 2007, as they are more likely to harbor unpatched vulnerabilities that can be exploited. Let’s examine a few attacks commonly instigated by outdated applications such as Microsoft Office 2007.
Attacks Due to Outdated Systems/Applications
Using outdated software like Microsoft Office 2007 can expose users to various security risks and make them vulnerable to different types of attacks. Some common attacks associated with Microsoft Office 2007 include the following:
Malicious Macros:
Microsoft Office applications, including Office 2007, support macros, which are scripts that automate tasks. If a user enables macros without verifying the source or legitimacy of the file, it can lead to the execution of malicious code, potentially compromising the system’s security.
Document-Based Exploits:
Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office file formats, such as Word documents (.doc), Excel spreadsheets (.xls), or PowerPoint presentations (.ppt). By crafting a malicious document, they can exploit vulnerabilities within Office 2007 and execute arbitrary code or deliver malware when the user opens the file.
Social Engineering Attacks:
Cyber attackers commonly employ phishing emails, spear phishing, and various social engineering techniques to deceive users into opening malicious Office documents or clicking on harmful links.. Such attacks may aim to steal sensitive information, install malware, or gain unauthorized access to the system.
Remote Code Execution (RCE):
Attackers can exploit unpatched vulnerabilities in Office 2007 to remotely execute arbitrary code, gaining control over the targeted system. This can result in data breaches, unauthorized access, or the installation of additional malware.
Zero-Day Exploits:
Zero-day exploits refer to vulnerabilities that are unknown to the software vendor or for which no security patches are available. Due to the lack of support for Office 2007, users are at an increased risk of falling victim to attacks that exploit any zero-day vulnerabilities discovered in the software. The lack of ongoing support means that these potential security risks will remain unaddressed, leaving users exposed to potential threats leveraging these unknown vulnerabilities. Upgrading to a more recent version is crucial to ensure ongoing security updates and protection against emerging risks.
Discover Outdated Systems/Applications with SanerNow Continuous Posture Anomaly Management
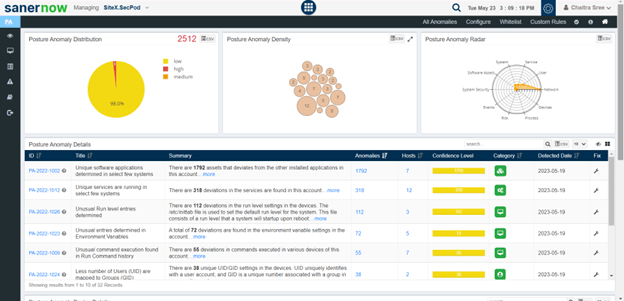
SanerNow scanners scan the organization for the anomalies present in your organization and list down the findings in the posture anomaly database.
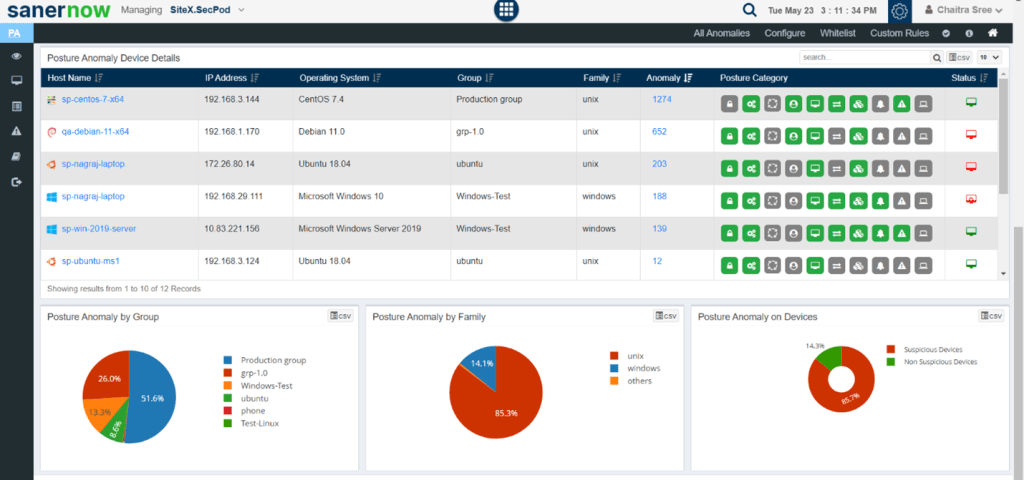
The dashboard will contain information about the anomalies detected, devices in which anomalies are there, categorizes them based on group, family, and more.
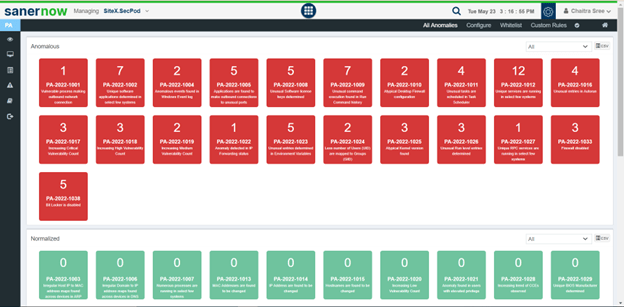
After detecting all anomalies in an IT environment, click on the “All anomalies” section. Here, you will encounter pages categorized as anomalous and normalized. A color-coded format represents these, where red indicates the presence of an anomaly, and green denotes the absence of anomalies based on the specific categorization.
When you scroll down further, you will find three subgroups under the outdated category, namely- outdated software applications, operating systems, and service packs.
These would automatically be present in the anomalous column when the scanner finds any outdated applications in your organization.
Conclusion
To ensure the highest level of security we strongly recommend organizations still using Office 2007 should upgrade to newer version. By doing so, they can benefit from the latest security features, bug fixes, and compatibility improvements, thus reducing the risk of cyber threats and ensuring a more secure computing environment.