In today’s interconnected digital landscape, protecting sensitive data has become more critical than ever. Full disk encryption emerges as a fundamental security measure in safeguarding confidential information against unauthorized access and data breaches. By encrypting every bit of data stored on a computer’s disk drive, this robust security solution ensures that even if a device falls into the wrong hands, the data remains unintelligible without the appropriate decryption key. As cyber threats continue to evolve and data privacy regulations become increasingly stringent, understanding the significance of full disk encryption is paramount for individuals and organizations alike in maintaining data confidentiality and mitigating the risks of unauthorized data access will be easier with patch management tool.
Data Security: Full disk encryption ensures that all data stored on a device is protected from unauthorized access. In the event of theft or loss, encrypted data remains unreadable without the encryption key.
Compliance Requirements: Many regulations and compliance standards, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), require organizations to implement encryption to protect sensitive data.
Prevention of Data Breaches: Full disk encryption prevents unauthorized users from accessing data even if they gain physical access to the device. This helps mitigate the risk of data breaches in case of lost or stolen devices.
Protection against Malware: Encryption can prevent malware from accessing and exfiltrating sensitive data from the device, thereby enhancing overall security posture.
Confidentiality: Full disk encryption ensures the confidentiality of data, including personal and sensitive information, by rendering it unreadable without the decryption key.
Overall, full disk encryption is a critical security measure to safeguard data privacy and protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
How to achieve full disk encryption?
In the Linux environment, the Linux Unified Key Setup (LUKS) serves as a robust solution for encrypting entire block devices and external storage devices. Encryption can be implemented in two scenarios: during the initial Linux installation and after the installation is complete. However, it is highly recommended to opt for encryption during the operating system installation process for enhanced security.
Note: Full hard drive encryption is exclusively feasible when performed during the Linux operating system installation. This ensures a comprehensive and integrated security approach.
Scenario 01: Enabling full hard drive encryption during installation of Ubuntu 22.10
The most straightforward method to encrypt the drive is during the Linux installation process. This approach guarantees smooth operation without encountering errors and ensures the thorough encryption of all partitions.
-
- After the configuration of memory selection, keyboard layout, etc. In the “Installation Type” step. Select “Erase disk and install Ubuntu“.
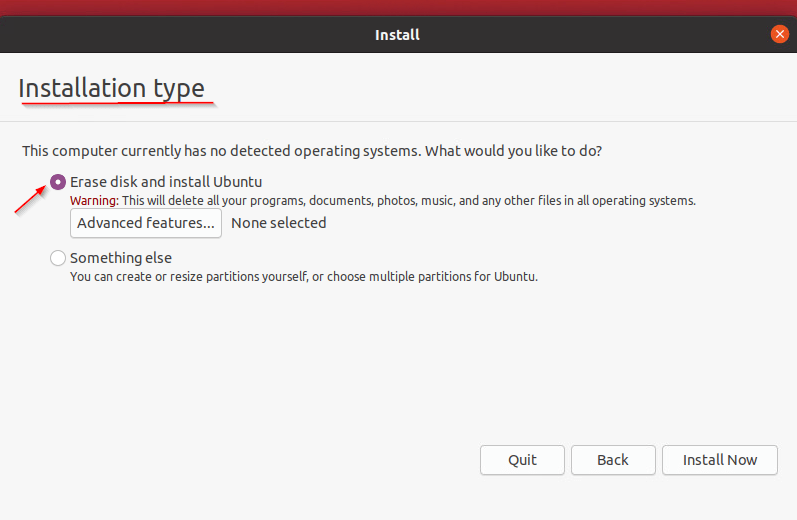
- Click the “Advanced Features” button
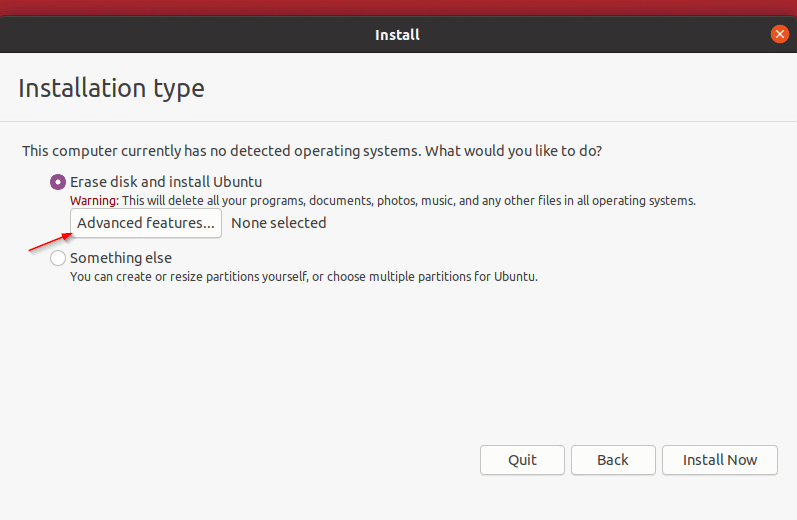
- Select the option “Use LVM with new Ubuntu installation“, then check the box “Encrypt the new Ubuntu Installation for security“, then click on “OK“, and click on “Install now” button.
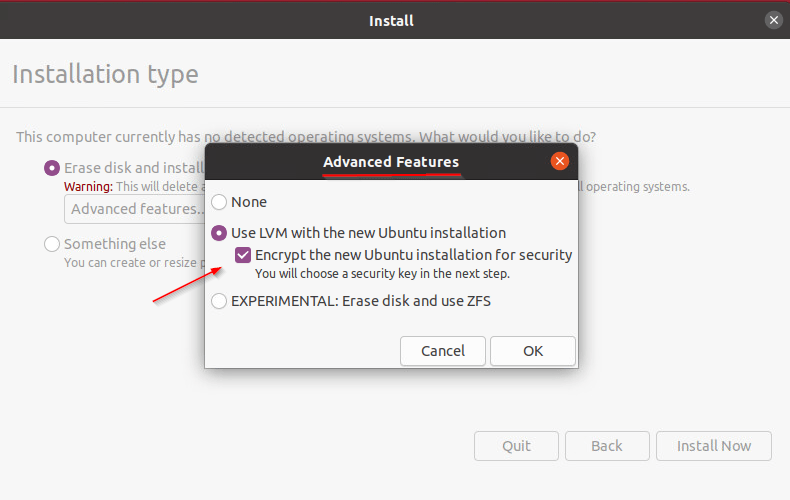
- Then enter a security key and confirm it, then click on “Install Now“.
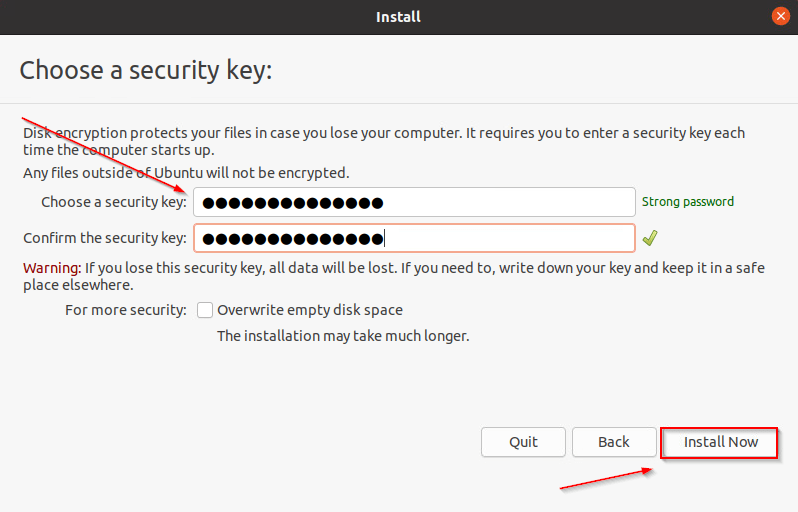
- After clicking on “Install Now”, there will be a prompt, Click on “Continue“.
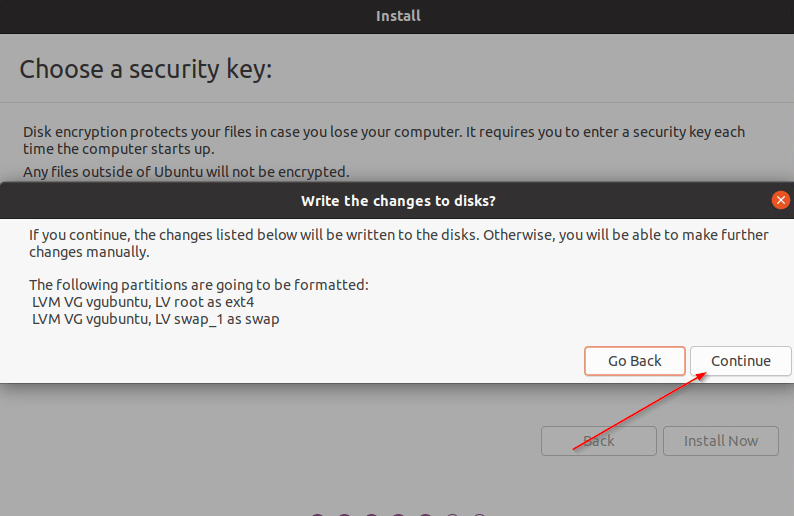
- Continue the installation process as prompted.
- After the completion of the process operating system will be installed and discs will be encrypted.
- Reboot the system.
- After the booting process, you have to enter the decryption key and click on “Enter”. After that, the discs will be unlocked.
- After the configuration of memory selection, keyboard layout, etc. In the “Installation Type” step. Select “Erase disk and install Ubuntu“.
Scenario 02: Encrypting Drives After OS Installation
If the operating system is already installed, it’s possible to encrypt the home directory and swap spaces without reinstalling the operating system.
By default, Linux stores most user data in the home directory for regular files, while the swap space holds sensitive information used for virtual memory management. Encrypting both the users’ home directory and swap space is advisable for enhanced security.
Caution: Encrypting files while logged in with your own account can lead to file corruption. Therefore, to encrypt the home directory, create a new user account with administrative privileges. Execute the following command to create a new user with administrative privileges:
$ sudo adduser encryption_user $ sudo usermod -aG sudo encryption_user
Encrypting home directory
After logging in with the encryption_user created in the previous command, follow these steps to encrypt the home directory.
-
- In Terminal execute the below command. It will install encryption utilities ‘encrypt-utils’ and cryptsetup.
$ sudo apt install ecryptfs-utils cryptsetup With the below command, you can see the contents/files that going to be encrypted.$ sudo ls -ldir_name
Where dir_name is the directory that you want to encrypt.- Start the encryption process by executing the following command
$ sudo ecryptfs-migrate-home -u username
whereusernameis the name of your user whose home directory you want to encrypt. - Enter the passphrase in the prompt, enter the user account’s login password when prompted, and hit “Enter”.
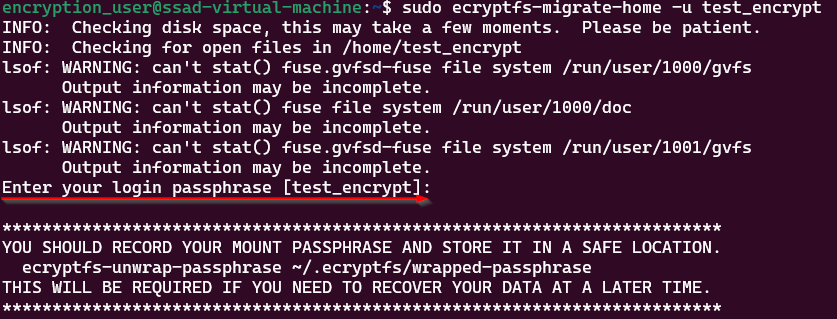
- The process will take some time if no errors below message you will get in the terminal.
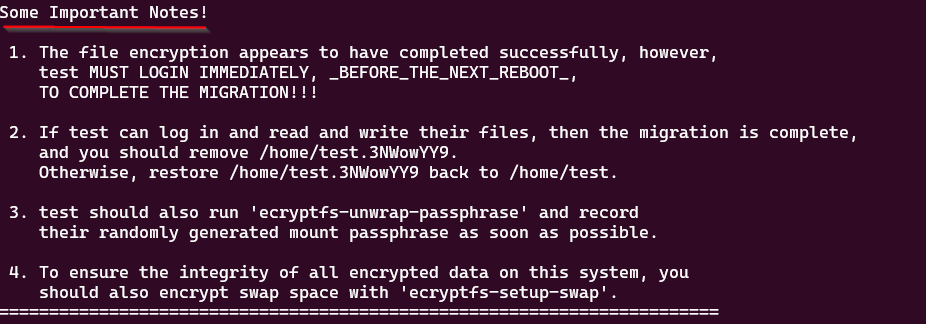
Note: Note: The user should log in to the encrypted user account to complete the encryption process before rebooting. After encryption, it’s crucial to verify if you can read and write files. If successful, the migration is complete, and you should proceed to remove the directory as suggested in the “Some Important Notes!“
-
After logging into your regular profile and checking if you can read and write files, you will need to record the encryption passphrase in the pop-up window and confirm it by clicking the “Run this action now” button. This will open a Terminal window, where you will be required to enter your password, after which a passphrase for your home directory will appear.
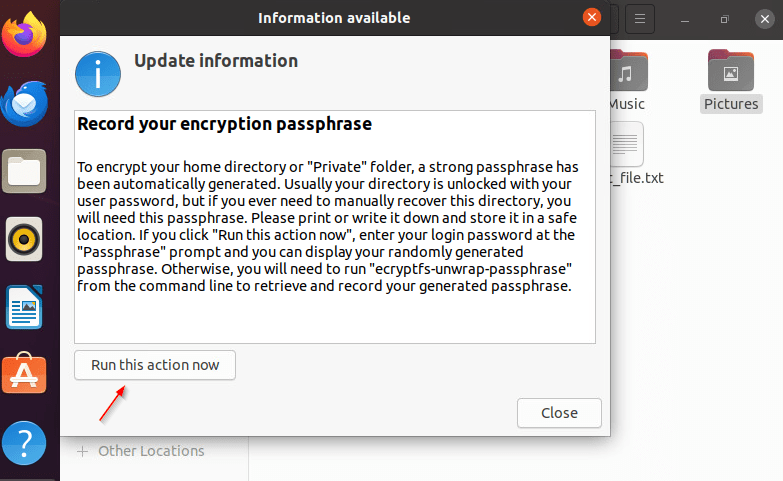
- The recovery passphrase can also be revealed by executing the below command.
$ sudo ecryptfs-unwrap-passphrase - Save the recovery password and keep it somewhere safe.
- In Terminal execute the below command. It will install encryption utilities ‘encrypt-utils’ and cryptsetup.
Encrypting swap space
-
- List the swap space by executing the below command.
$ swapon -s - Execute the below command to encrypt the swap space.
$ sudo ecryptfs-setup-swap
- List the swap space by executing the below command.