Linux is the backbone of most modern business organizations and a massive network. Amazon, the largest cloud provider globally, runs its EC2 cloud computing platform on Linux. Currently, the Linux kernel employs 27.8 million lines of code, updated every year. Several new bugs or vulnerabilities appear whenever the kernel is added with new lines of code. As a result, there is a substantial increase in the threat surface, which needs proactive solutions to keep the attack surface minimum. The bottom line is that any update to the Linux platform increases the attack surface. This can be avoided by using a Linux vulnerability management software.
On the other hand, incorporating any new mechanisms and dependencies should be handled with great care as they can directly affect the size of the attack surface against Linux. Security gaps may appear on Linux systems like any other operating system. However, every OS has different ways to deal with them. The security flaws on Linux are purely logical and capable enough to make an application vulnerable to severe attacks.
What are the Different Types of Threats on your Linux Systems?
Most software security updates provided by Linux distributors will quickly solve programming defects, including vulnerabilities. In case of weak configuration, Linux patches notify the respective software with the logical steps that explain how it should execute. It enhances the security of both operating systems and devices. Despite adopting careful security measures, vulnerabilities appear in a large, complex Linux computing environment. Therefore, it is essential to understand the impact of vulnerabilities and different threats on a Linux-distributed network by using Linux Vulnerability Management Tool.
Exploits due to Unpatched Vulnerabilities:
One of the best attack surfaces for a cyber attacker is unpatched vulnerabilities. If an IT team fails to apply timely patches and run regular software updates, there is a space for exploiting the vulnerabilities. An unpatched application may enable malicious code and cause severe threats on a wide variety of Linux-based systems.
Regular patching and updates are necessary because unpatched software creates vulnerabilities through which attackers exploit the computing devices in a network. Cyber attackers could enable ransomware-style encryption and other dangerous malicious code using the unpatched vulnerabilities, especially on Linux-based storage devices. This can be rectified by using Linux Vulnerability Management.

Malware Attacks
Vulnerabilities in a Linux operating system will result in various attack vectors such as viruses, worms, ransomware, rootkits, etc. Cyber attackers will use the existing vulnerabilities to inject malicious code into a system without the user’s consent. They might steal sensitive business data or compromise the devices.
Cybercriminals can further spread the attacks beyond the corporate network, and the attack often goes undetected by end-users. In most cases, attackers silently assemble compromised OS into botnets and pose a threat to the entire network.
Denial of Service Attacks (DoS)
A Linux operating system acting as an interface between hardware and software might stop responding to the end user’s legitimate requests due to a denial-of-service attack. The attack focuses on shutting down a device, making it inaccessible to the end-users.
Today’s operating system may undergo denial-of-service attacks by a distributed network of several thousands of automated agents. It is challenging to mitigate, as the attack is always massive. For instance, an attacker sends countless network requests, which results in the repeated use of system requests. It makes the server acknowledge every request, exhausting all the resources. However, modern IT security technologies and tools have developed various mechanisms to defend against DoS attacks by using Linux Vulnerability Management software.
The Intrusion of Linux Network
Various types of network intrusion occur when an attacker gains access to the devices, creating a security threat. If authorized users neglect to follow the security policies in the devices, it leads to network intrusion. With the help of vulnerabilities, external individuals pose as legitimate users and exploit the end-user credentials.This can be pre Also, some undercover users gain supervisory control of the devices and penetrate the system and access controls. In an organization, malicious insiders also misuse their privileges for cybercriminal activities. Therefore, testing and validating your Linux operating systems is essential. It is an ongoing process, and it depends on the risk and priority of the business organizations.
Make your Linux Systems Free from Vulnerabilities using SanerNow.
SanerNow vulnerability manager offers a comprehensive solution to all your vulnerability management needs. It is powered by the world’s largest vulnerability database of more than 160,000 security checks. SanerNow provides real-time continuous scanning, assessment, prioritization, and remediation of vulnerabilities for Linux systems. SanerNow also offers additional tools along with vulnerability management tool to help keep track of the effectiveness of your Linux security network. With SanerNow, you can,
- Manage vulnerabilities on Linux systems from detection to remediation
- Gain complete visibility and control over the IT assets
- Align and comply with major industry security benchmarks, namely HIPAA, PCI, ISO, and NIST
- Fix misconfigurations and missing configurations
- Monitor security checks and apply strong security controls
- Detect and respond to threat indicators
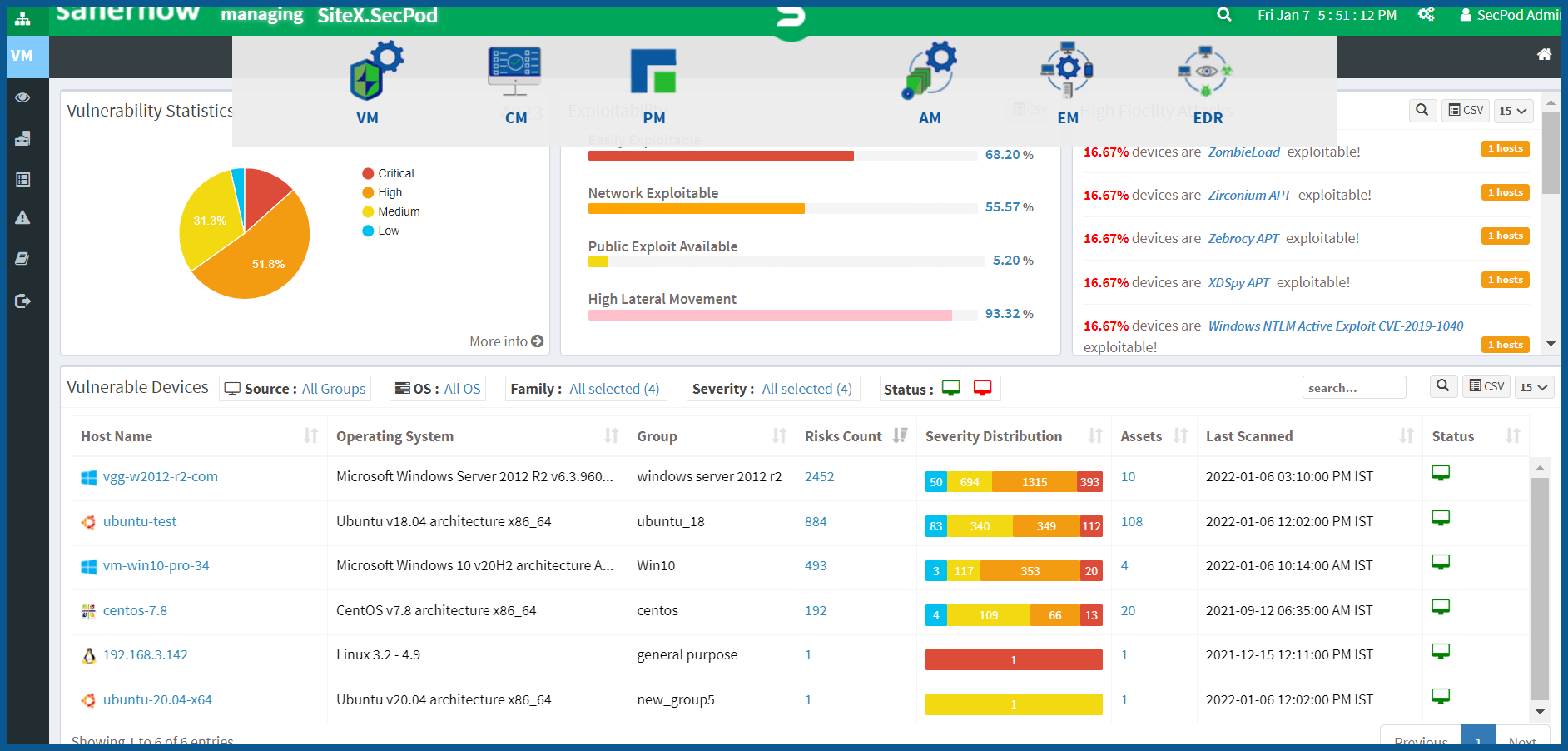
Explore SanerNow’s vulnerability management capabilities at the comfort of your place by scheduling a quick demo for Free.