Lemon Duck is a monerocrypto-mining malware. This malware was first spotted in China but has hence spread to other parts of the world. Lemon Duck starts with single infection and spreads rapidly across the entire network. Converting the resources of an organization into cryptocurrency mining slaves. However, a vulnerability management tool detects this malware.
Researchers from TrapX-Labs have reported that Lemon Duck has especially targeted IoT Devices running Windows 7 Embedded in its campaigns. Microsoft declares that no further updates is released for Windows 7. In the absence of regular updates, the severity of the upcoming malware attacks on systems running Windows 7 could be disastrous. Also, it is distressing to indicate that 200 million devices are still using the old Windows 7. However, a patch management tool can patch and update these devices.
Lemon Duck malware written in Python using PyInstaller for compilation. However, this malware’s main strategy is fileless infection using PowerShell modules. Moreover, the infection on the network happens through the exploitation of a critical SMB vulnerability(CVE-2017-0144) and brute-force attacks.
Malware Capabilities
- Delivers XMR miners to mine for cryptocurrency.
- Uses fileless infection techniques.
- Steals information such as computer name, machine UUID, MAC address, and IP address, etc. and sends them to the C&C server.
- Modifies Windows Firewall settings to open port 65529/TCP on complex machines.
- Implants 32- and 64-bit versions of malicious DLL components to removable and network drives.
- Register shortcut (LNK) files in the startup folder to execute malicious javascript upon reboot.
- Executes PowerShell code remotely using WMI.
- Uses open-source tools such as PowerDump, freerdp, and Mimikatz to carry out various actions.
- Includes an Installation Tracking C2 module which reports the machine profile and status of every executed module to the C2 server. Uses another Continuous Monitoring C2 module to send details about the compromised user accounts, machine configuration, user privilege and exploitation or mining payloads status.
- Leverages the Windows Scheduled Tasks mechanism to download fresh copies of malicious scripts at regular intervals.
Malware Infection and Propagation Methods:
1) EternalBlue Exploit (CVE-2017-0144): Lemon Duck scans the network on TCP Port 445 using the PingCastle scanner to look for devices with the EternalBlue vulnerability. Lemon Duck launches ‘SMB Exploitation Module’ on devices that are vulnerable to the EternalBlue exploit.
2) Windows LNK Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2017-8464): LemonDuck infects removable USB drives and network drives by implanting malicious DLLs in a folder along with a shortcut (LNK) file. When a user opens the drive in any application which parses the .lnk Shortcut file, the shortcut executes the malicious DLL component.
3) Mimikatz module and PassTheHash attacks: A powershell script is used to download a Mimikatz module from a specific URL. The Mimikatz module is used for collecting user information. Moreover, this information along with hard-coded lists of passwords and NTLM hashes is used to launch PasstheHash(PtH) and brute force attacks.
4) RDP brute force attacks: Firstly, Lemon Duck includes an RDP module which scans for the open servers using the default RDP Port 3389 and attempts to login with the “administrator” user name. Secondly, a freerdp module downloaded with the Mimikatz module, provides a list of hardcoded passwords which are used in RDP brute force attacks.
5) Brute forcing of MS-SQL servers: A script included in the malware checks for an open port 1433/TCP used by the Microsoft SQL service and tries to brute force against the “SA”(system administrator) user account.
SanerNow lists the potential targets for malwares in an enterprise network (shown in the figures below).
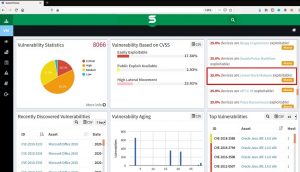 Fig1. SanerNow listing of potential targets in an organization for Lemon Duck Malware
Fig1. SanerNow listing of potential targets in an organization for Lemon Duck Malware
Fig2. Details about Lemon Duck Malware
However, SanerNow detects and mitigates the vulnerabilities which uses as infection vectors for spreading Lemon Duck Malware. Moreover, download SanerNow and keep your systems updated and secure.
General Recommendations
1) Keep your systems up-to-date with the latest security patches.
2) Use strong and complex passwords
3) Refrain from opening any suspicious emails or links.
4) Manage network shares and disable anonymous logins.