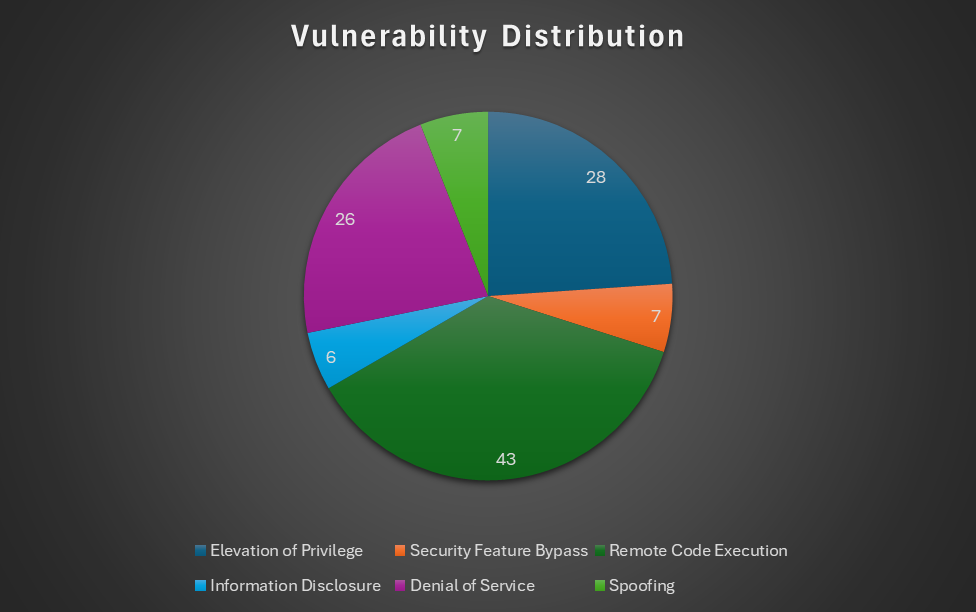
This month, Microsoft released security updates addressing 118 vulnerabilities, of which 5 were publicly disclosed zero days, and 3 were critical RCE flaws. Two of the zero days are known to have been actively exploited. The chart below offers some insight into the types of vulnerabilities found.
You can detect and remediate such vulnerabilities instantly with a patch management tool.
Zero Day Vulnerabilities
The first two flaws mentioned were actively exploited.
CVE-2024-43573: Windows MSHTML, Platform Spoofing, CVSS 6.5 – The MSHTML platform was previously used by Internet Explorer and the Legacy version of Microsoft Edge, and its components are still present in Windows. According to Microsoft, the MSHTML platform is used by Internet Explorer mode in Microsoft Edge and other applications through web browser control.
Though unconfirmed, this issue may bypass a previous vulnerability that exploited MSHTML to spoof file extensions in alerts shown when opening files. A similar MSHTML spoofing vulnerability was disclosed last month, where attackers used Braille characters in filenames to disguise PDF files.
CVE-2024-43572: Microsoft Management Console, Remote Code Execution, CVSS 7.8 – This vulnerability enabled malicious Microsoft Saved Console (MSC) files to execute remote code on affected devices, and the fix involved blocking untrusted MSC files from being opened.
Though this flaw is known to have been actively exploited in attacks, the method used remains unclear.
CVE-2024-6197: Open Source Curl, Remote Code Execution, CVSS 7.5 – This vulnerability is in libcurl and could allow commands to be executed when Curl connects to a malicious server that presents a specially crafted TLS certificate. The fix involved updating the libcurl library, which is included with the Curl executable in Windows.
CVE-2024-20659: Windows Hyper-V, Security Feature Bypass, CVSS 7.1 – This UEFI bypass vulnerability which affects virtual machines could allow attackers to compromise both the hypervisor and the secure kernel. An attacker would need physical access to the device and must reboot it to exploit the vulnerability.
CVE-2024-43583: Winlogon, Elevation of Privilege, CVSS 7.8 – This privilege escalation vulnerability could allow attackers to gain SYSTEM-level access on Windows devices. Mitigation steps involve keeping a Microsoft first-party Input Method Editor (IME) enabled, preventing the exploitation of any vulnerabilities related to third-party IMEs.
Products Affected
- .NET and Visual Studio
- .NET,.NET Framework, Visual Studio
- Azure CLI
- Azure Monitor
- Azure Stack
- BranchCache
- Code Integrity Guard
- DeepSpeed
- Internet Small Computer Systems Interface (iSCSI)
- Microsoft ActiveX
- Microsoft Configuration Manager
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Management Console
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft Office Visio
- Microsoft Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol
- Microsoft WDAC OLE DB provider for SQL
- Microsoft Windows Speech
- OpenSSH for Windows
- Outlook for Android
- Power BI
- RPC Endpoint Mapper Service
- Remote Desktop Client
- Role: Windows Hyper-V
- Service Fabric
- Sudo for Windows
- Visual C++ Redistributable Installer
- Visual Studio
- Visual Studio Code
- Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock
- Windows BitLocker
- Windows Common Log File System Driver
- Windows Cryptographic Services
- Windows EFI Partition
- Windows Hyper-V
- Windows Kerberos
- Windows Kernel
- Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers
- Windows Local Security Authority (LSA)
- Windows MSHTML Platform
- Windows Mobile Broadband
- Windows NT OS Kernel
- Windows NTFS
- Windows Netlogon
- Windows Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Windows Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)
- Windows Print Spooler Components
- Windows Remote Desktop
- Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service
- Windows Remote Desktop Services
- Windows Resilient File System (ReFS)
- Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS)
- Windows Scripting
- Windows Secure Channel
- Windows Secure Kernel Mode
- Windows Shell
- Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service
- Windows Storage
- Windows Storage Port Driver
- Windows Telephony Server
- Winlogon
If you’re using any of these products, you should patch them immediately! Microsoft’s Security Update Guide details mitigations and patches for each vulnerability. You can also use tools to help you apply those patches.
Instantly Fix Risks with SanerNow Patch Management
SanerNow patch management is a continuous, automated, and integrated software that instantly fixes risks exploited in the wild. The software supports major operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS, as well as 550+ third-party applications.
It also allows you to set up a safe testing area to test patches before deploying them in a primary production environment. SanerNow patch management additionally supports a patch rollback feature in case of patch failure or a system malfunction.
Experience the fastest and most accurate patching software here.


