It’s been a calm year so far for patches! January saw no zero days, February only saw two, and March has brought us another month with zero zero days, so to speak. Microsoft’s Patch Tuesday states that out of the 60 flaws found, two are critical, and none were previously disclosed or actively exploited – which means no updates for the CISA KEV.
Despite the distinct lack of wildly exploited vulnerabilities (so far), there are still some interesting flaws in the catalogue. One non-critical bug that stands out is CVE-2024-20671, a Security Feature Bypass vulnerability that could prevent Microsoft Defender from starting if exploited! Defender can’t defend your system if it’s compromised, so make sure to get its defenses back up by updating your Windows device. A patch management tool helps patch these vulnerabilities effectively.
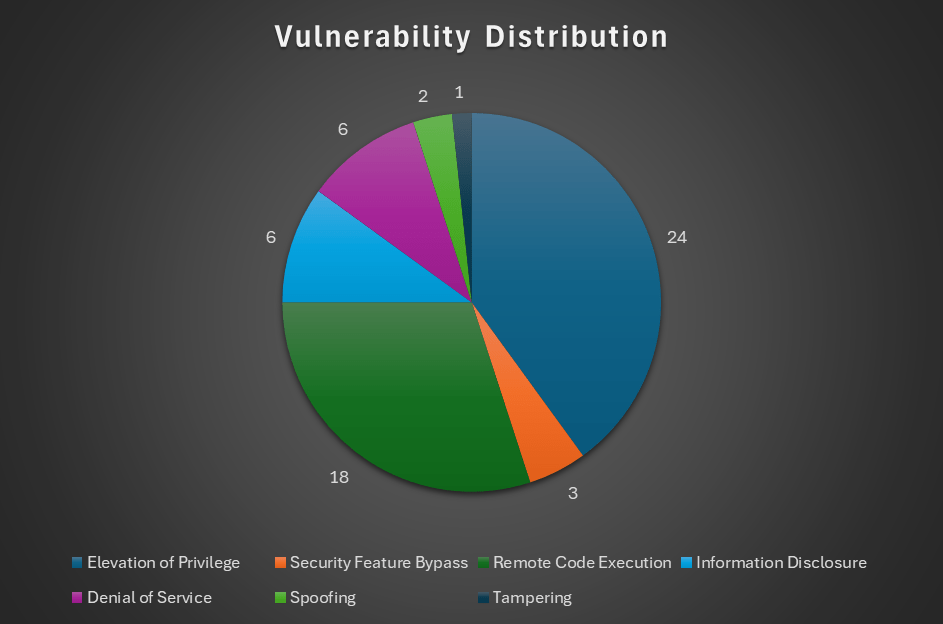
The distribution of flaw types is shown below.
Critical Vulnerabilities
Two critical flaws were patched, both for Windows Hyper-V.
CVE-2024-21407: Microsoft Windows Hyper-V, Remote Code Execution – A Critical flaw rated 8.1 on the CVSS scale. Exploiting this vulnerability allows attackers from a Hyper-V guest to execute code on the host server. They need authentication on a guest virtual machine and then send specific requests to the host. Though complex, successful exploitation can lead to server code execution, so patching is crucial.
CVE-2024-21408: Microsoft Windows Hyper-V, Denial of Service – Another Critical flaw scoring 5.5 on the CVSS scale. It enables attackers to disrupt a Hyper-V guest virtual machine, affecting the host’s functionality. As it’s a local DoS attack, Microsoft considers it less likely to be exploited.
Products Affected
- .NET
- Azure Data Studio
- Azure SDK
- Intel
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Microsoft Azure Kubernetes Service
- Microsoft Django Backend for SQL Server
- Microsoft Dynamics
- Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based)
- Microsoft Edge for Android
- Microsoft Exchange Server
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Intune
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft QUIC
- Microsoft Teams for Android
- Microsoft WDAC ODBC Driver
- Microsoft WDAC OLE DB provider for SQL
- Microsoft Windows SCSI Class System File
- Open Management Infrastructure
- Outlook for Android
- Role: Windows Hyper-V
- Skype for Consumer
- Software for Open Networking in the Cloud (SONiC)
- Visual Studio Code
- Windows AllJoyn API
- Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver
- Windows Composite Image File System
- Windows Compressed Folder
- Windows Defender
- Windows Error Reporting
- Windows Hypervisor-Protected Code Integrity
- Windows Installer
- Windows Kerberos
- Windows Kernel
- Windows NTFS
- Windows ODBC Driver
- Windows OLE
- Windows Print Spooler Components
- Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service
- Windows Telephony Server
- Windows Update Stack
- Windows USB Hub Driver
- Windows USB Print Driver
- Windows USB Serial Driver
If you’re using any of these products, you should patch them immediately! Check out how to do that in the solutions section below.
Solutions
Microsoft’s Security Update Guide details mitigations and patches for each vulnerability. You can also use tools to help you apply those patches. SanerNow Vulnerability Management, Risk Prioritization, and Patch Management detect and automatically fix vulnerabilities with risk-based remediation. Use SanerNow to keep your systems updated and secure.

