Too much network traffic? Is a PDF reader or word processing application making a strange internet connection? Often such observations are considered as anomalies to detect a threat or an attack but not prevent them.
We often encounter situations where numerous software is installed in a machine, whether in-use or not-in-use, personal devices connected to the organization’s network, ports, or services running in computer systems whether necessary or not. Employees and users have different software preferences accounting for their work requisites. Such anomalies often cause uncertainties and unnecessary surprises for our IT and Security Administrators, who constantly strive to keep the organization secure, keep track of inventories, help with software installation and steadily keep them up-to-date. Finding anomalies in an organization and removing such deviations can help reduce the attack surface and prevent cyberattacks.
Anomaly detection is the first step towards gaining visibility to bring order to business. Chaos and clutter of technologies are complicated to maintain. Do we need these inconsistent applications? Why are so many ports open, numerous processes running, or different firewalls configured across devices? A patch affects only one system in the organization; why is it so? Often we see that a unique operating system or application is running on that device, which also results in vulnerabilities and misconfigurations anomalies that are avoidable.
Often security is perceived as looking at one device at a time rather than analyzing them collectively. Outliers can be computed when a set of parameters from all devices are observed together. There are various ways in which anomalies can be determined. Let us look at each with an example.
Outlier-based Anomalies
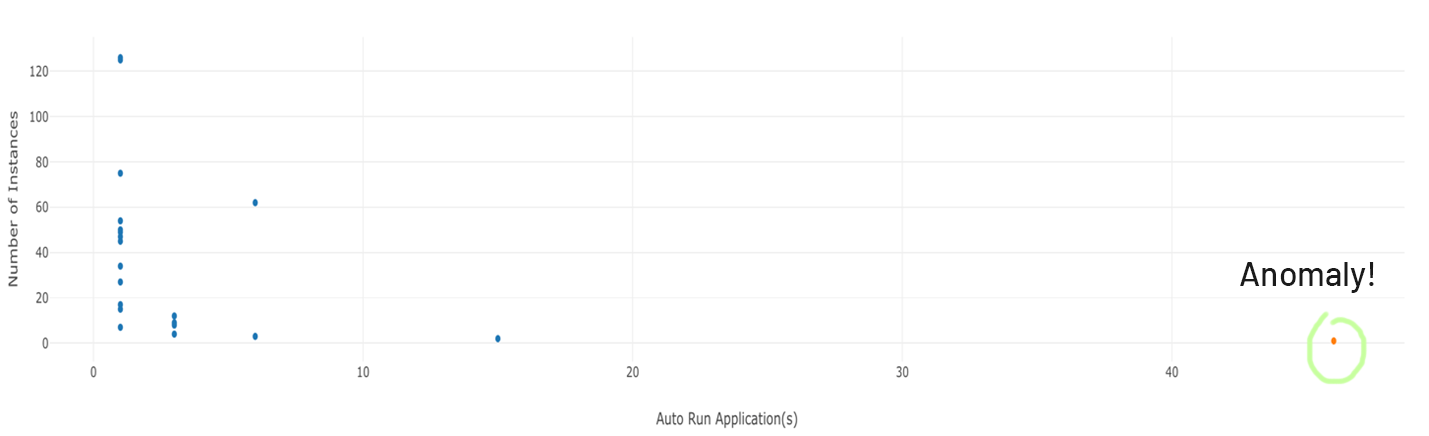
Clustering parameters such as Software assets versions and their signatures, Run Command History, Firewall settings, Scheduled Task, Service, Autorun applications, IP Forwarding Status, UID GID mapping, Kernel parameters, RPC, Software licenses, or High CPU or RAM usage are analyzed, and deviations are observed as anomalies.
Rule-based Anomalies
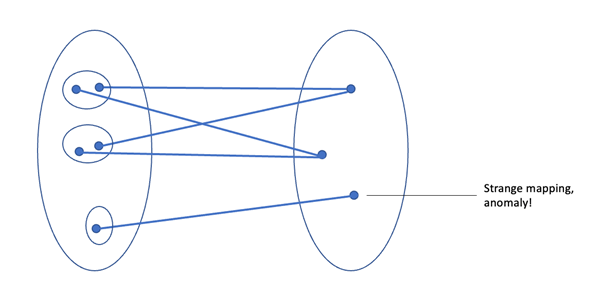
Mapping ARP entries and DNS Cache entries reveal interesting finds when devices are analyzed collectively. If any process is connected to more than one foreign port in the account, it is marked as an anomaly. Each anomaly is marked with confidence to add value to the anomalous finding.
Data-trend based Anomalies
When we collect some parameters over a period, and if there is an abnormality identified in those parameters, we term that particular parameter’s instance as an anomaly. For example, changes in the hostname, MAC address, and IP address, sudden changes in the number of Critical, High, Medium, and Low vulnerabilities, and variations in CCEs are distressing for any organization.
Deviations from Standard Configurations
There are 40+ checks provided by Continuous Posture Anomaly Management to test whether devices are set with different configurations. For example, when we analyze VPN software used by a team of 50 employees, we may observe that OpenVPN is used by 13 employees, VPN software suggested by the IT administrator is used by 36 employees, and 1 employee uses hide.me.VPN. It raises a concern that why there are three different VPN software in use.
Visibility to 1000+ parameters in devices and detection of anomalies eases decision-making for IT and Security administrators. Simple and intuitive dashboards can help solve the deviations with a collection of relatable actions. Whitelisting anomalous findings that are expected in the devices can bring a standard to be followed while computing anomalies.
Conclusively, anomalies should be reduced in an organization for better IT and security administration. Certainties and predictability of device configuration, software vulnerabilities, and compliance issues can be comprehended if administrators and CISOs gain substantial visibility of the organization’s assets. Anomalies in art create beautiful discoveries, but in business, we need order.
To learn more about Continuous Posture Anomaly Management, click here.