Let’s continue from where we left off last week, and will go through the behavior patterns of the next versions of the Cerber Ransomware.
Cerber3.0: Cerber3.0 RIG-V exploit kit is an updated version of Cerber2.0. After the release of Cerber2, security vendors released some decryptors to decrypt the files that were encrypted by the ransomware. Since then developers of Cerber took time and made a newer version. The new version is more sophisticated in its execution and has strong encryption compared to Cerber2.0. After distribution and getting into execution mode, Cerber scans the computer for targeted files and starts to encrypt. Upon encryption, the encrypted files will not be available to use for the user, and ransom notes will be dropped in each folder

These files are named as # HELP DECRYPT #.html, and # HELP DECRYPT #.txt. These ransom notes, as usual, have the necessary information on how to decrypt the encrypted files. The encrypted files will be renamed into a random 10 alphanumeric characters, with a new extension .cerber3 attached to each file.
Like previous versions of Cerber, this version also executes the below command. which will causes the loss of all the backup copy of local files.
C:\Windows\System32\wbem\WMIC.exe shadowcopy delete
Cerber’s Registry Entries:
Adds an entry of its extension –Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\FileExts\.cerber3
HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\[random.exe "%AppData%\{ransom}\[random].exe"
Cerber4.0: Unlike Cerber3.0 this version of ransomware does not use any extension in particular like .cerber, .cerber2, or .cerber3. As per our analysis, the ransomware has been adding a file extension with 4 alphanumeric characters. Some of the samples that were tested, added an extension like “a9fc“, “bb99“. The encryption mechanism has been drastically improved compared to the previous versions. The ransomware observed to be avoiding encrypting security related products. It also has the capability to avoid some serious detection mechanisms too. Below is the picture which highlights the version of the ransomware in its ransom note.
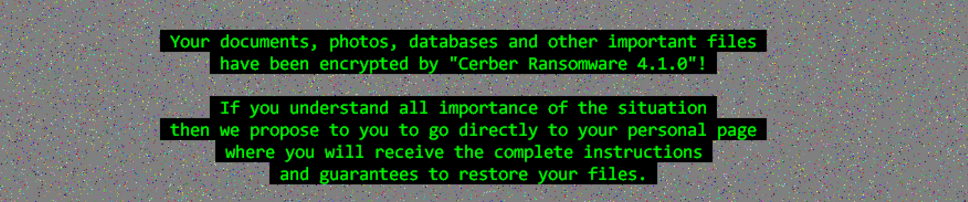
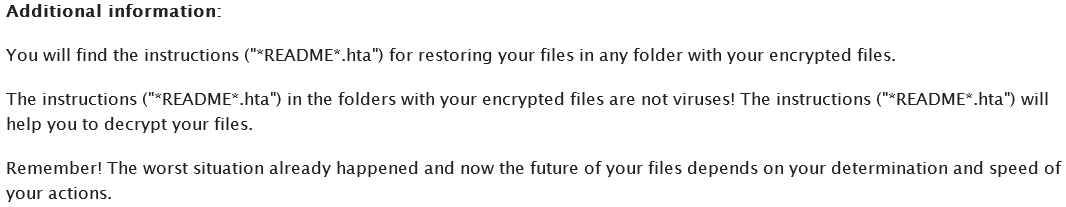
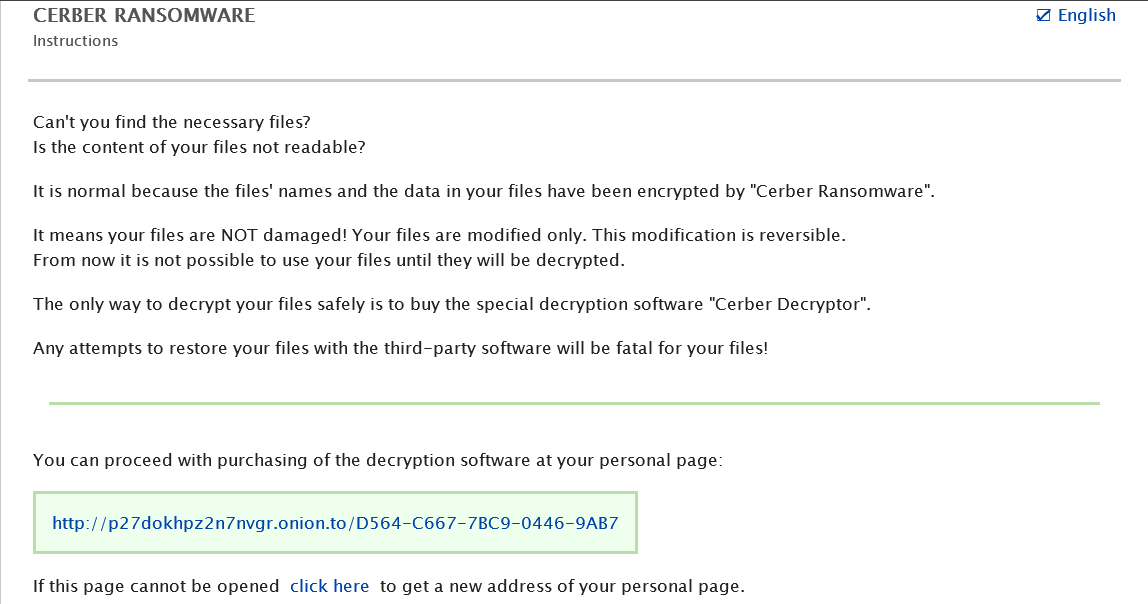
In Cerber4.0, we have observed the release of different subversion i.e from 4.1.0 – 4.1.6. All different releases include a series of improvements in encryption mechanism. Dropping various components in each folders makes it impossible to remove from the computer. Some versions changed the registry values and also added some new random entries w.r.t cryptography. The only way to decrypt the files is using “cerber decryptor” as mentioned in the ransom note that will drop after encryption. Below is the picture of a ransom note.
The ransomware drops ransom notes with file names “_HELP_HELP_HELP_[random] .hta” and “_HELP_HELP_HELP[random]_ .txt“. Just like the previous versions, there is not much of a change in the note.
Luckily this version does not have ‘vssadmin‘ command enabled which is used to delete the shadow copies of the user backups. Hence using shadow copies there is a chance to restore encrypted files.
Cerber5.0: Cerber 5.0 was first detected back in late 2016 and was using RIG-V exploit for infection. Cerber is the most profitable and highly active ransomware. To keep the researchers busy, developers of the Cerber ransomware quickly released this version which is more intelligent in its behavior.
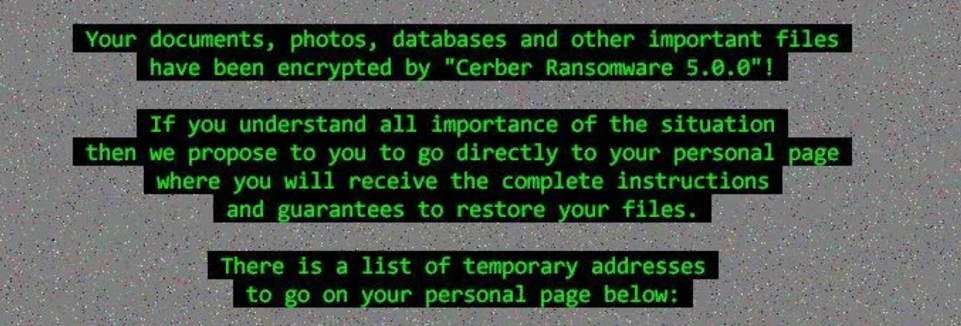
This ransomware jumbles the file names after encryption and the extension used here is completely random. i.e extension will differ from each victim’s computer. The encryption method has changed a bit where Cerber will skip the file encryption if the file size is below 2.6kb in size. Below is the picture of the ransom note it leaves behind.
Cerber 5.0 observed to drop ransom notes with file names “[random]?README[random]?.hta“, and
“[random]?README[random]?.txt“. In our analysis, we observed that malicious Cerber’s code multicasts messages to all IP addresses via User datagram protocol(UDP). which was contacting some of the command and control servers which are listed below.
91.119.216.30-31 , 91.120.55.30-31 and
91.121.217.0-255 , 91.121.219.0-166
Saner in Action:
The snapshots below shows how Saner detects Cerber ransomware in real-time.
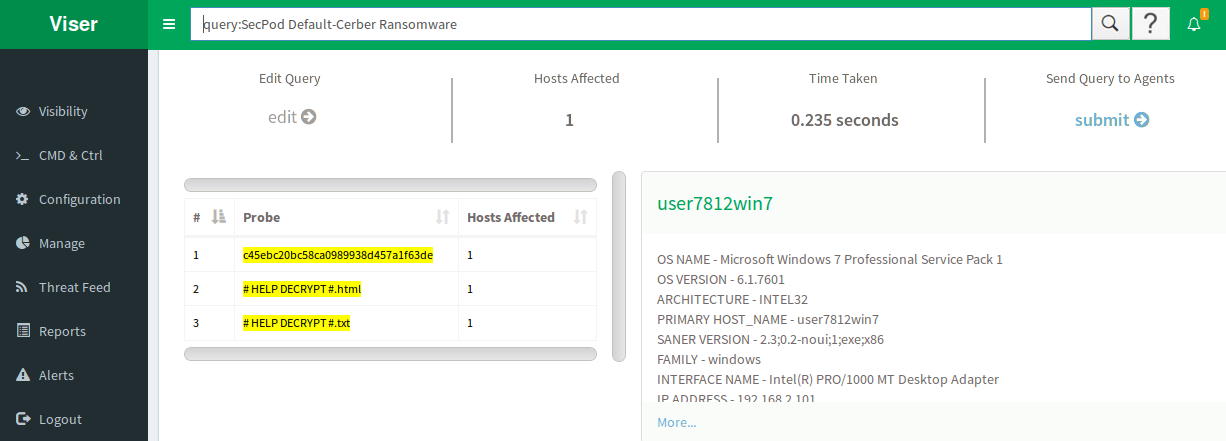
We recommend updating your operating system and software on a regular basis. This reduces the probability of becoming a victim of Cerber, as it uses various methodologies of spreading. Recognize Cerber malware alerts and trust Saner updates.
Keep looking at this space for continuation on Cerber’s other variants and its distribution methodology, i.e Part-3.