Yet another large scale widespread ransomware attack immobilized many organizations around the world. Last month we had seen the infamous WannaCry taking over the world by affecting more than 3 million computers in over 150 countries, with the UK’s national health service, and German state railways among those hardest hit. This is why it’s important to have a vulnerability management solution to avoid such ransomware attacks.
This time it is Ransomware Petya vulnerability (NotPetya, Petna, or SortaPetya), well let’s not call it as wannacry 2 please, because this nasty piece of ransomware is not like traditional ransomware, Petya does not bother to encrypt any files, instead, it forces a system shutdown and after a reboot the entire hard drive’s master file table (MFT) is encrypted. A patch management tool can patch this vulnerability and avoid this ransomware attack.
How does it work?
Petya is known to be spreading using the infamous NSA Eternalblue exploit. Unlike WannaCry ransomware which used to infect systems would in turn scan and infect other systems which caused it to spread rapidly and exponentially. The Current Petya ransomware attack is different in the sense that the exploit it uses are only used to spread across a local network rather than the internet.
Another method used by the Petya is to use the Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC) to execute itself directly on the remote machine, using stolen credentials.
"Petya was deployed onto possibly millions of computers by hacking popular Ukrainian Accounting software 'MeDoc' then using the automatic update feature to download the malware onto all computers using the software. Although MeDoc being the initial infection vector is unconfirmed" - Malwaretech
The last method Petya attempts is to copy itself as a copy of psexec.exe to the remote machine’s ADMIN$ folder. If it is successful, the malware attempts to start psexec.exe using a remote call to run as a service.
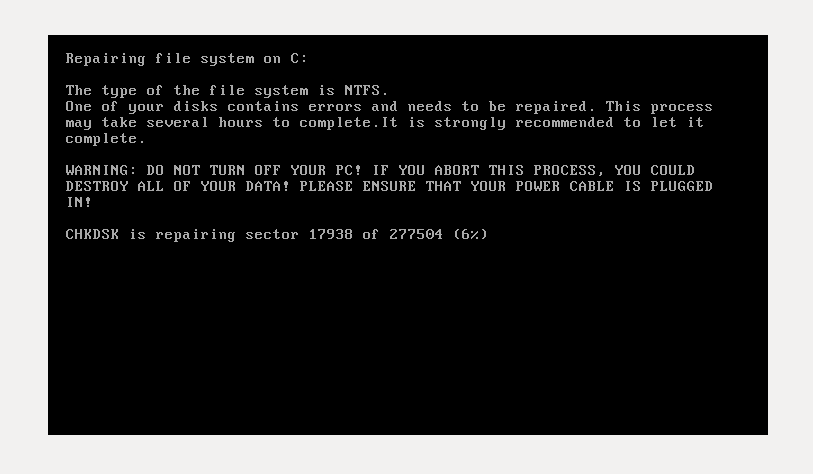
Once the system infected with the ransomware, it creates a scheduled task (shutdown.exe /r /f) to force shutdown and reboot the system. In one hour system will reboot and ransomware will start to encrypt files. Below is a screenshot which shows that ransomware is pretending like checking the integrity of your hard disk, meanwhile it encrypts the entire hard disk. This will restrict access to the full system by seizing information about file system.
"Petya ransomware successful in spreading because it combines both a client-side attack (CVE-2017-0199) and a network based threat (MS17-010)".
Never Pay Ransom!!!!
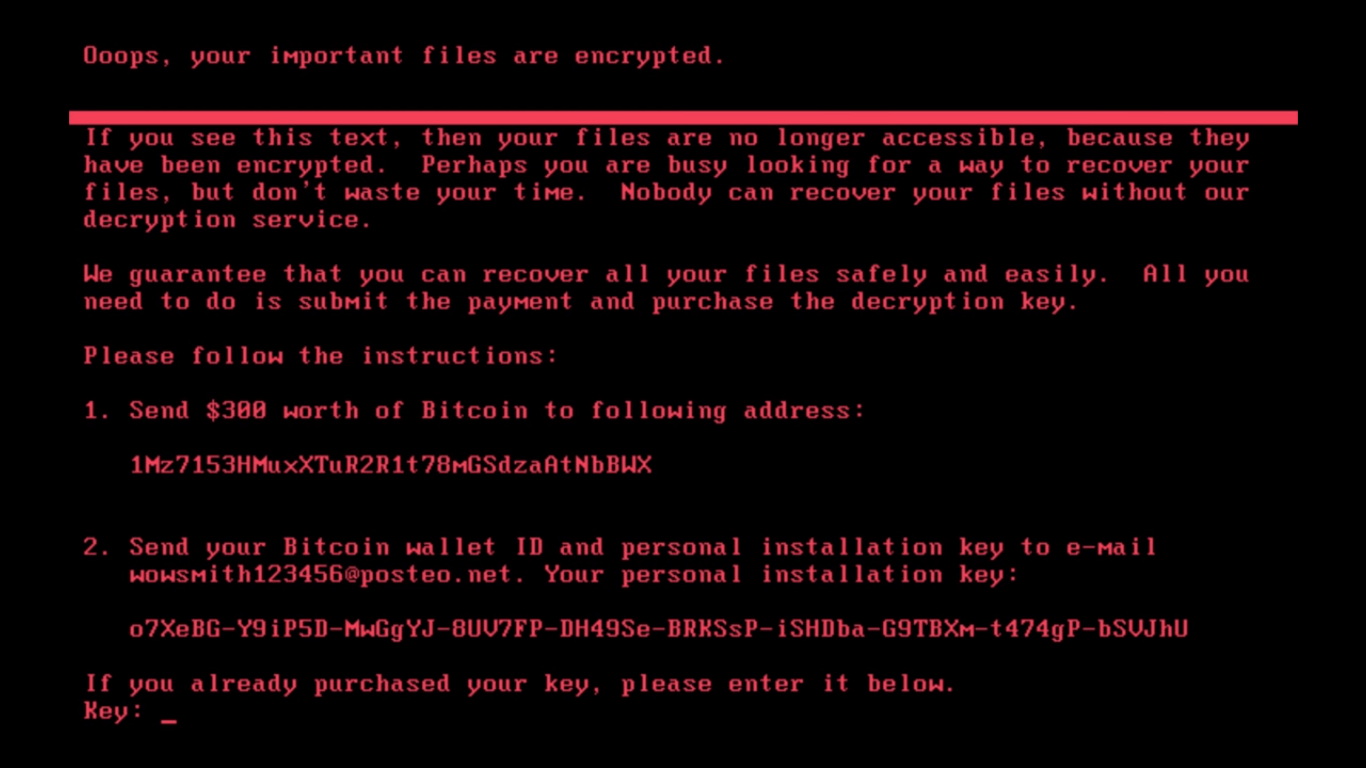
After encrypting the MFT, ransomware is demanding ransom worth of $300 in bitcoin. Below is the screenshot of the ransom note.
Though if you manage to pay the ransom to the given bitcoin address, you wont be getting back the decryption key as the “customer service” email address shut down so there’s no way to get the decryption key to unlock your files anyway.
The Kill-Switch:
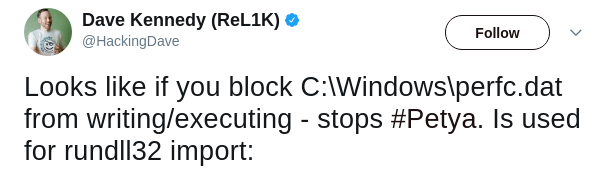
Researchers have found a kill switch which will apparently stops petya execution. The Kill switch is a file under “C:\Windows\perfc” which created without any extension. Since the file perfc used as import in runtime32.dll, blocking write access to the file would stop the execution.
Twitterati says:
Who is affected by Ransomware Petya??
The list includes Russian state-owned oil giant Rosneft, Ukrainian state electricity suppliers, “Kyivenergo” and “Ukrenergo”. Large firms in Europe and the US, including the advertising firm WPP, French construction materials company Saint-Gobain and Russian steel and oil firms Evraz and Rosneft. The food company Mondelez, legal firm DLA Piper, Danish shipping and transport firm AP Moller-Maersk and Heritage Valley Health System.
Precautions to take against “Petya”:
- Disable SMBv1: vulnerability exploited through SMBv1.
- Immediately patch your Windows with Microsoft’s recently released fix.
Petya is using the EternalBlue exploit by NSA(MS17-010). It is never too late to learn from the mistakes, keep the systems updated and secured by patching with security updates on a regular basis.
Trust SecPod Saner updates by applying security updates. Download Saner now and keep your systems updated and secure.