The fundamental property in public key cryptography is that public keys are really public. It provides anyone without causing any impact on security. This fundamental property is completely failing by the ROCA attack. The vulnerability arises from a software library Infineon Technologies AG used in cryptographic hardware for RSA key generation. All keys generated using this library are prone to ROCA attacks. This library uses various hardware many domains use, including trusted boot devices, electronic citizen documents, software package signing, TLS/HTTPS keys, authentication tokens, and PGP. Vulnerability Management tool can reduce these vulnerabilities.
This vulnerability is present in the library in use by NIST FIPS 140-2 and CC EAL5+, two internationally adopting cryptographic standards. It can be characterized by a specific structure of the generated RSA primes, which makes factorization practically possible for commonly used key lengths, including 1024 and 2048 bits. No physical access to the affected device is required, and only the knowledge of a public key is necessary. The primes generated allow for fast detection of vulnerable keys, even in large datasets. The key length ranges considered practically factorizable are 512 to 704 bits, 992 to 1216 bits, and 1984 to 2144 bits. 4096-bit RSA key is not practically factorizable now, but it can be possible if the attack is improving on its own.
Affected Versions:
The Infineon RSA library 1.02.013 in Infineon Trusted Platform Module (TPM) firmware, such as versions before 0000000000000422 – 4.34, before 000000000000062b – 6.43, and before 0000000000008521 – 133.33.
Impact:
An attacker can compute a valid private key from the value of a public key based only on a certificate. This makes everything possible. The private key can be misused to do anything on your behalf including encrypting traffic, decrypting the traffic, and impersonating the website and other related attacks. Usage scenario, availability of the public keys, and the lengths of keys used are the three main factors determining the actual impact of the vulnerability.
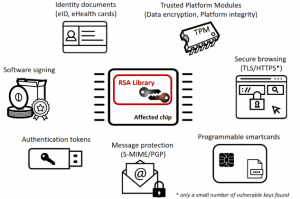
The usage domains affected by ROCA:
Detection:
The detection is finding the usage of a chip with a vulnerable library. However, The only reliable and recommended way is RSA key pair generation on the device and testing the public key against the ROCA flaw with the provided tools mentioned below,
- Offline: https://github.com/crocs-muni/roca
- https://keytester.cryptosense.com/
- https://keychest.net/roca
Solution:
Fixed TPM firmware versions are as follows, upgrade to the latest as soon as possible.
- 0000000000000422 – 4.34
- 000000000000062b – 6.43
- 0000000000008521 – 133.33
Protection:
Due to the complexity of this issue, it’s difficult to patch completely, but there are few mitigation methods. Windows users can address this issue by applying security updates issued by Microsoft. Google, HP, and Lenovo have also released some mitigation methods and firmware updates for their software products. The below-mentioned links describe the mitigation strategies and fixed version details provided by different vendors.
- https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-us/security-guidance/advisory/ADV170012
- https://support.lenovo.com/de/en/product_security/len-15552
- https://sites.google.com/a/chromium.org/dev/chromium-os/tpm_firmware_update
SanerNow detects these vulnerabilities and automatically fixes it by applying security updates for Windows users. Therefore, Download Saner now and keep your systems updated and secure.